The Rise of AI Robots: How Intelligent Automation is Reshaping Industries

Introduction
We stand at the precipice of a new industrial revolution, one driven not by steam or silicon, but by intelligence itself. The silent, tireless march of AI robotics and intelligent automation is no longer the stuff of science fiction; it’s a tangible reality unfolding in our factories, warehouses, hospitals, and even on our farms. This convergence of artificial intelligence—the “brain”—and sophisticated machinery—the “body”—is creating a new generation of robotic systems that can perceive, learn, and adapt in ways previously unimaginable.
The conversation has shifted from if robots will change our world to how they are actively reshaping it. From the intricate dance of collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside humans on assembly lines to autonomous robots navigating chaotic warehouse floors, AI-powered automation is redefining efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
In this comprehensive exploration, we will journey through the landscape of next-gen automation. We’ll demystify the core concepts, explore the groundbreaking robotic applications transforming key industries, and confront the critical questions about the future of work and the ethical considerations that come with creating intelligent machines. Prepare to discover how this powerful fusion of AI and robotics is not just an upgrade to existing processes but a fundamental rethinking of how we produce, deliver, and live.
The Core of the Revolution: What Exactly is Intelligent Automation?
To understand the current wave of robotics advancements, we must first distinguish between traditional automation and the intelligent automation that’s causing such a stir.
For decades, automation has meant pre-programmed machines performing repetitive, high-volume tasks with speed and precision. Think of the large, caged robotic arms on a classic car assembly line. They are incredibly effective at their one specific job but lack any ability to adapt to changes or handle variability. If a part is misaligned, the traditional robot will likely continue its task, potentially causing errors or damage.
Intelligent automation, fueled by AI machine learning robots, is a paradigm shift. It infuses robotic systems with the ability to handle the unpredictable. Here’s the difference:
- Sensing & Perception: Modern AI integration robotics uses advanced sensors, computer vision, and LiDAR to perceive the world in rich detail. An AI robot can identify different objects, read text, and detect anomalies in real-time.
- Learning & Adaptation: Through machine learning algorithms, these robots learn from experience. They can refine their movements, improve their accuracy over time, and adapt their processes based on new data without human intervention.
- Decision-Making: Unlike their predecessors, AI robots can make autonomous decisions. An autonomous mobile robot (AMR) in a warehouse can independently decide the most efficient path to a package, navigating around unexpected obstacles like a fallen box or a human worker.
This combination of perception, learning, and decision-making is the engine driving the most significant automation trends we see today. It’s the difference between a machine that follows a script and one that can improvise, problem-solve, and collaborate.
Related: Mastering Prompt Engineering to Unlock AI’s Potential
The Factory of the Future: AI and Manufacturing Reinvented
Nowhere is the impact of AI robotics more profound than in manufacturing. The concept of the smart factory, or Industry 4.0, is becoming a reality, where digital and physical systems are deeply intertwined, creating a highly responsive and efficient production environment.
Precision and Productivity: The New Age of Industrial Automation
While industrial automation has been a cornerstone of manufacturing for years, AI has supercharged its capabilities. AI and manufacturing are now inseparable concepts, leading to unprecedented levels of precision and operational intelligence.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze data from sensors on robotic arms and other machinery to predict when a part is likely to fail. This allows for maintenance to be scheduled before a breakdown occurs, saving millions in unplanned downtime.
- AI-Powered Quality Control: High-resolution cameras combined with computer vision algorithms can inspect products on the assembly line with superhuman speed and accuracy. They can detect microscopic defects, ensure perfect alignment, and verify component placement, reducing waste and ensuring higher quality products.
- Generative Design: AI can now even participate in the design process. Engineers can input design goals and constraints (e.g., weight, material, cost), and an AI can generate thousands of optimized design variations, often yielding highly efficient and innovative solutions that a human might not have conceived.
Meet Your New Coworker: The Rise of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Perhaps the most significant shift in workforce automation is the emergence of cobots. Unlike their heavy-duty industrial ancestors that were locked away in safety cages, collaborative robots are designed to work safely in close proximity to human employees.
These lightweight, versatile arms are equipped with advanced sensors that allow them to stop immediately upon making contact with a person. This safety feature unlocks a new level of human-robot collaboration. Cobots excel at tasks that are ergonomic risks for humans, such as:
- Lifting and holding heavy parts for inspection.
- Performing repetitive screwing, gluing, or polishing tasks.
- Tending machines, freeing up skilled operators for more complex work like programming and quality assurance.
Cobots aren’t about replacing workers; they’re about augmenting their capabilities. They take on the dull, dirty, and dangerous aspects of a job, reducing physical strain and allowing human talent to be focused on problem-solving, creativity, and oversight—tasks where humans still far outshine any AI.
Related: Mastering AI Workflow for Productivity and Automation
Revolutionizing the Supply Chain: AI in Logistics and Warehousing
The e-commerce boom has placed unimaginable strain on the global supply chain. The demand for next-day—or even same-day—delivery requires a level of speed and accuracy that is nearly impossible to achieve with human labor alone. This is where AI in logistics has become a game-changer.
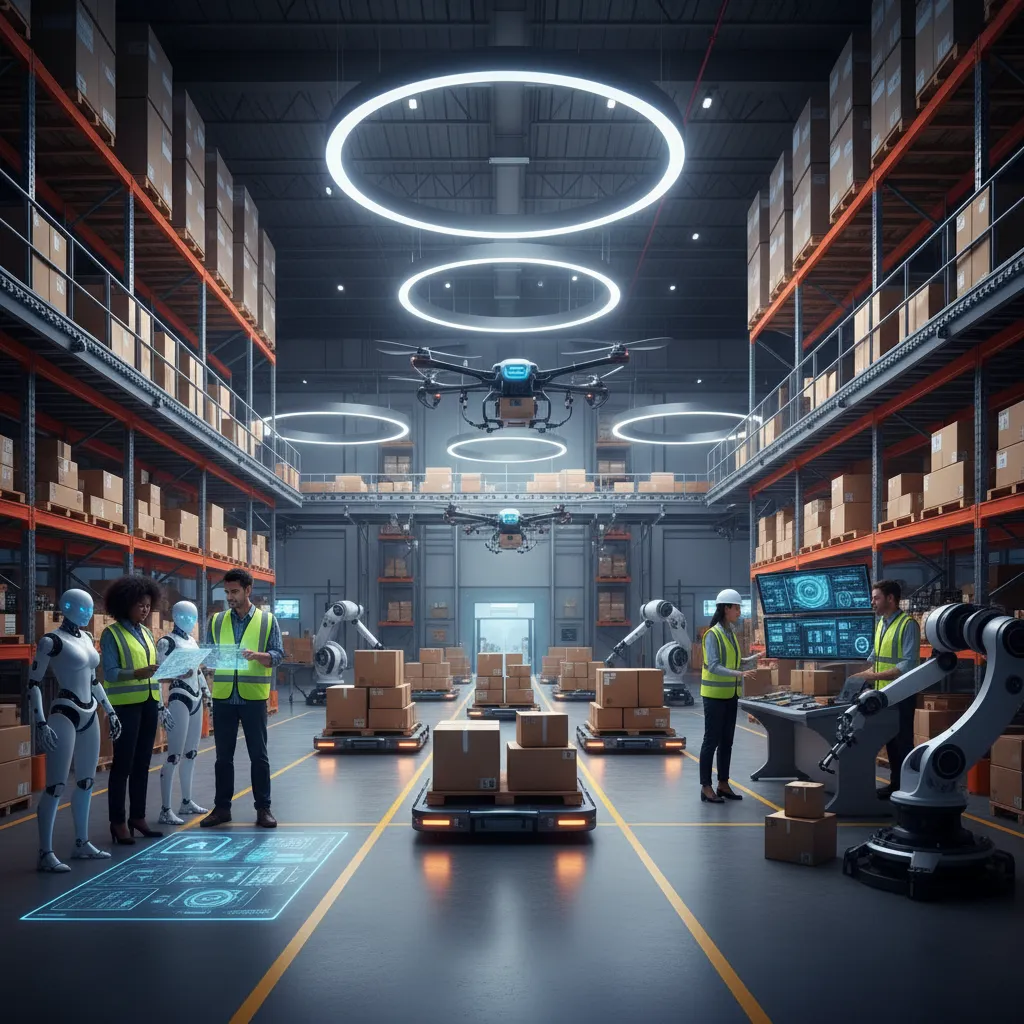
The Autonomous Warehouse
Walk into a modern fulfillment center, and you’ll witness a symphony of intelligent automation. The backbone of this operation is often a fleet of autonomous robots, specifically Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs).
Unlike Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) that follow fixed magnetic strips on the floor, AMRs use AI, LiDAR, and cameras to map the warehouse and navigate dynamically. They can:
- Retrieve Goods: Instead of workers walking miles of aisles, AMRs bring entire shelving units (“pods”) directly to a stationary worker’s picking station.
- Sort Packages: Robotic arms with advanced vision systems can identify, pick up, and sort thousands of packages per hour, routing them to the correct outbound truck with near-perfect accuracy.
- Manage Inventory: Autonomous drones can fly through the warehouse during off-hours, scanning barcodes and using computer vision to perform a complete inventory count in a fraction of the time it would take humans.
This level of AI-powered automation drastically increases order fulfillment speed, reduces errors, and improves worker safety by minimizing manual material handling.

From First Mile to Last: AI-Driven Solutions on the Move
The intelligence doesn’t stop at the warehouse door. AI is optimizing the entire logistics network. Sophisticated algorithms analyze traffic patterns, weather conditions, and delivery schedules in real-time to plot the most efficient routes for trucks, saving fuel and time. AI also powers demand forecasting, helping companies anticipate purchasing trends and position inventory in the right locations before orders are even placed, which is a core tenet of modern AI-driven solutions.
Beyond the Factory Floor: AI Robotics in Emerging Sectors
While manufacturing and logistics are the epicenters of the robotics revolution, the robotics industry trends show a rapid expansion into nearly every corner of our economy and society. This is where we see the most diverse and sometimes surprising robotic applications.
A New Standard of Care: AI in Healthcare Robotics
The potential for AI in healthcare robotics is immense, promising greater precision for surgeons and better care for patients.
- Surgical Assistance: Systems like the Da Vinci surgical robot are now being enhanced with AI. This advanced robotics platform allows surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with greater control and vision. AI adds layers of intelligence, such as highlighting critical anatomy or stabilizing for a surgeon’s natural hand tremors.
- Lab Automation: Robotic systems are automating the highly repetitive tasks in medical labs, such as moving test tubes and analyzing samples, which increases throughput and reduces the risk of human error.
- Patient Care and Companionship: Service robots and even early-stage humanoid robots are being developed to assist in elder care facilities. These cobots can help with tasks like reminding patients to take medication, providing mobility support, and offering social interaction to combat loneliness.

Sowing the Seeds of the Future: Robotics in Agriculture
Agriculture is undergoing a high-tech transformation. Robotics innovation is helping to solve major challenges like labor shortages and the need for more sustainable farming practices.
- Precision Agriculture: Autonomous tractors, guided by GPS and AI, can plow fields, plant seeds, and dispense fertilizer with centimeter-level accuracy. This reduces waste and minimizes environmental impact.
- Crop Monitoring: Drones equipped with multispectral cameras fly over fields, using AI to analyze crop health, identify pests or disease, and assess irrigation needs long before the human eye could detect a problem.
- Automated Harvesting: One of the biggest challenges in agriculture is harvesting delicate produce like strawberries or lettuce. New robots with soft, dexterous grippers and advanced computer vision are being developed to perform this task, ensuring produce is picked at peak ripeness.

The Human Element: Workforce Automation, AI, and Future Jobs
No discussion of AI and robotics is complete without addressing the elephant in the room: what does this mean for human jobs? The narrative of “robots are coming for our jobs” is pervasive, but the reality is far more nuanced. While some roles, particularly those involving repetitive manual labor, will be automated, this technological shift is also creating entirely new categories of work.
The focus is shifting from replacement to augmentation. Workforce automation is poised to eliminate tasks, not necessarily jobs. By handing over the monotonous and physically demanding work to robots, human workers are freed up to focus on higher-value activities that require uniquely human skills: critical thinking, complex problem-solving, creativity, emotional intelligence, and customer interaction.
This transition necessitates a massive investment in reskilling and upskilling. The AI future jobs landscape will include roles we are only just beginning to define:
- Robot Fleet Managers: Professionals who oversee the operation, maintenance, and optimization of entire fleets of autonomous robots.
- Automation Ethicists: Experts who help design and implement robot ethics AI frameworks to ensure intelligent systems operate fairly and safely.
- AI/Human Interaction Designers: Specialists who create intuitive interfaces and workflows for effective collaboration between people and their new robotic coworkers.
The future of work isn’t a world without human jobs; it’s a world where humans work smarter, empowered by intelligent machines.
Related: What is Apple Intelligence? Your Guide to AI in iOS 18
Navigating the New Frontier: The Ethics and Challenges of AI Robotics
As with any powerful technology, the rise of AI robotics comes with significant challenges and ethical questions that we must navigate carefully.
- Algorithmic Bias: If the data used to train an AI is biased, the robot’s decisions will also be biased. This is a major concern in areas like hiring or security, where a biased robot could perpetuate societal inequalities.
- Accountability and Safety: When an autonomous system makes a mistake that causes harm, who is responsible? The owner, the user, the manufacturer, or the programmer? Establishing clear legal and ethical frameworks for accountability is one of the most pressing challenges in the field of robot ethics AI.
- Data Privacy: Many service robots, especially in homes and healthcare, collect vast amounts of sensitive data. Ensuring this data is secure and used ethically is paramount to building public trust.
- Economic Disruption: The transition to an automated workforce, if not managed properly with social safety nets and robust education programs, could exacerbate economic inequality.
Addressing these issues proactively is essential for ensuring that the development of advanced robotics benefits all of humanity.
Related: Neuromorphic Computing: Brain-Inspired AI Tech
Conclusion: Rising with the Robots
The era of intelligent automation is here, and its momentum is only growing. From the intricate dance of cobots in smart factories to the tireless work of autonomous robots in our supply chains, AI robotics is fundamentally reshaping the industrial and social fabric of our world. This transformation goes far beyond simple robotic process automation; it represents a new partnership between human ingenuity and machine intelligence.
We are witnessing the evolution of robot technology from a tool that simply follows commands to a collaborator that can perceive, learn, and contribute in dynamic environments. The challenges, particularly concerning AI future jobs and robot ethics, are real and require our careful attention.
However, the potential for progress is undeniable. By embracing this wave of innovation, investing in our skills, and guiding its development with wisdom and foresight, we can build a future where intelligent automation elevates human potential, solves some of our most pressing challenges, and creates opportunities we can only just begin to imagine. The rise of the robots isn’t a story about our obsolescence; it’s the beginning of a new chapter in our own evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between AI and robotics?
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is the “brain” that provides the ability to think, learn, and make decisions. Robotics is the “body”—the physical machine or structure that can move and interact with the world. An AI robot combines both, using AI to intelligently control its physical actions.
Q2. What are the 3 main types of robots?
While there are many classifications, three common categories are: Industrial Robots (like large arms used in manufacturing), Service Robots (which assist humans in tasks like cleaning, delivery, or healthcare), and Collaborative Robots (Cobots) (designed to work safely alongside humans).
Q3. Will AI robots take all human jobs?
No, it’s highly unlikely they will take all jobs. History shows that technology automates tasks, not entire professions, and creates new jobs in the process. AI robots are expected to handle repetitive and physically demanding tasks, allowing humans to focus on roles requiring creativity, critical thinking, and social intelligence—skills that are very difficult to automate.
Q4. What are the main advantages of AI robotics?
The primary advantages include increased productivity and efficiency, improved quality and consistency, enhanced worker safety by taking over dangerous jobs, and the ability to operate 24/7. They can also perform tasks with a level of precision and scale that is impossible for humans.
Q5. What is an example of an AI robot?
A great example is the fleet of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) used in Amazon fulfillment centers. These robots use AI and machine vision to navigate the warehouse floor, identify the correct shelving units, and bring them to human workers for order picking, drastically speeding up the entire process. Another is Boston Dynamics’ Spot, a dog-like robot that can navigate complex terrain for inspection and data collection.
Q6. What are the ethical concerns of AI-powered robots?
Key ethical concerns include potential job displacement and economic inequality, algorithmic bias leading to unfair decisions, issues of accountability when an autonomous robot causes harm, data privacy concerns with robots that collect information in sensitive environments, and the safety and security of these complex systems.