Edge AI Explained: Powering Smart Devices & Real-time Intelligence

Introduction
In an increasingly connected world, the demand for instant insights and intelligent decision-making is skyrocketing. From the personalized recommendations on your smartphone to the critical safety features in autonomous vehicles, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. Yet, traditionally, AI’s immense processing power resided primarily in distant, powerful cloud data centers. This paradigm, while effective for many tasks, often grappled with latency, bandwidth limitations, and privacy concerns when dealing with the sheer volume of data generated at the “edge” – where devices and people interact with the physical world.
Enter Edge AI, a transformative technological leap that brings the power of artificial intelligence directly to these devices and the network edge. Imagine your smart home devices, factory sensors, or even medical wearables making intelligent decisions without constantly sending data back and forth to the cloud. This is the promise of Edge AI: to enable real-time AI processing, enhance privacy, and revolutionize how smart devices operate. It’s about more than just convenience; it’s about creating a faster, more secure, and more efficient intelligent ecosystem.
This comprehensive guide will demystify Edge AI, exploring what it is, how it works, its profound benefits, a myriad of Edge AI applications, the Edge AI challenges it faces, and its exciting future of Edge AI. Join us as we uncover how AI on device is unleashing the full potential of smart device AI and IoT AI, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in decentralized AI and distributed AI computing.
What Exactly is Edge AI? Demystifying the Decentralized Revolution
At its core, Edge AI is a methodology where AI algorithms, particularly machine learning models, are processed directly on a local device or server at the “edge” of a network, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud infrastructure. Think of it as moving the brain closer to the body parts performing the actions.
To fully grasp Edge AI, it’s essential to understand its foundational concept: Edge Computing. Edge computing refers to a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data. This proximity is critical because it significantly reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and enhances data privacy. When AI capabilities are integrated into this edge computing framework, we get Edge AI.
Historically, AI relied heavily on the cloud. Raw data from cameras, sensors, and other devices would be transmitted to powerful cloud servers, where AI models would analyze it and send back instructions or insights. While powerful, this cloud-to-edge data flow can introduce delays.

Edge AI flips this script. Instead of sending all data to the cloud, the trained AI model itself is deployed to an AI processing on edge device. This means the device can perform AI inference at the edge – making predictions or decisions based on new data – locally. This represents a significant shift towards decentralized AI and distributed AI computing, where intelligence isn’t confined to a single, distant hub but is spread across the network.
Consider a smart security camera. In a traditional cloud AI setup, every frame it captures might be sent to the cloud for facial recognition. With Edge AI, the facial recognition model resides on the camera itself. The camera processes the video stream locally, identifies a known face, and only then sends a small alert (e.g., “known person detected at front door”) to the cloud or your phone. This AI on device approach dramatically reduces the data transmitted and speeds up the response time.
This move to local processing is not about replacing cloud AI entirely but augmenting it. Cloud AI remains crucial for training complex models, storing vast datasets, and performing heavy-duty analytics. Edge AI, however, excels at immediate, context-aware decision-making where low latency AI is paramount.
The Mechanics of Edge AI: How Intelligence Moves Closer to the Source
The magic of Edge AI lies in how complex on-device machine learning models are optimized and deployed to resource-constrained devices. It’s a fascinating blend of hardware and software innovation.
1. Model Optimization: Making AI Lean
Before an AI model can run efficiently on an edge device, it often needs to be significantly optimized. Cloud-trained models can be enormous, requiring vast computational resources. For AI on device, these models undergo processes like:
- Quantization: Reducing the precision of the numbers used in the model (e.g., from 32-bit floating point to 8-bit integers) to save memory and speed up computation with minimal loss in accuracy.
- Pruning: Removing redundant or less important connections (weights) in neural networks.
- Knowledge Distillation: Training a smaller “student” model to mimic the behavior of a larger, more complex “teacher” model.
- Architecture Search: Designing compact, efficient neural network architectures specifically for edge environments.
- These techniques contribute to the rise of TinyML, a specialized field focused on enabling
machine learning on tiny microcontrollers and edge devices.
2. Specialized Hardware: The Brains of the Edge
Traditional CPUs in edge devices often aren’t efficient enough for sophisticated AI workloads. This has spurred innovation in specialized hardware designed for AI inference at the edge:
- AI Accelerators: Dedicated chips or modules, often integrated into System-on-Chips (SoCs), optimized for parallel processing of AI computations. These can be GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), NPUs (Neural Processing Units), or custom ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits).
- Low-Power Processors: Chips designed to perform complex tasks with minimal power consumption, crucial for battery-operated
IoT AIdevices. - Many modern smartphones, smart cameras, and industrial sensors now come equipped with these
microchip processing data on an edge devicecapabilities.

3. Software Frameworks and Runtime Environments
Deploying and running optimized AI models on diverse edge hardware requires specialized software. Frameworks like TensorFlow Lite and PyTorch Mobile allow developers to convert and deploy models efficiently. Runtime environments ensure these models can execute effectively on the device’s operating system, managing resources and interfacing with the hardware accelerators. This entire AI processing on edge workflow is designed to be streamlined, from model training in the cloud to its efficient execution on countless edge nodes.
Why Edge AI Matters: Unpacking the Benefits
The shift towards decentralized AI is driven by a compelling suite of advantages that address the limitations of purely cloud-based AI. Understanding these Edge AI benefits reveals why it’s becoming a cornerstone of modern technological infrastructure.
Real-time Intelligence and Low Latency
Perhaps the most compelling benefit of Edge AI is its ability to deliver real-time AI insights and actions. By processing data locally, the time taken for data to travel to a distant cloud server, be processed, and for instructions to return is eliminated. This low latency AI is critical for applications where even milliseconds matter:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars need to make instantaneous decisions about braking, steering, and obstacle avoidance. Waiting for cloud processing is simply not an option. [Related: The Electric Revolution: Guide to EVs & Sustainable Driving]
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing,
Edge AI in manufacturingcan detect defects on a production line or predict machinery failures instantly, preventing costly downtime. - Robotics: Robots performing delicate tasks or navigating complex environments rely on immediate sensory input processing.
Enhanced Privacy and Security
Sending sensitive data, like personal biometric information or proprietary industrial data, to the cloud raises significant privacy and security concerns. Privacy preserving AI edge processing mitigates these risks by keeping data local.
- Healthcare: Wearable devices monitoring patient vital signs can analyze data for anomalies on the device itself, only sending anonymized or aggregated alerts to medical professionals. This is crucial for
Edge AI in healthcare. - Smart Homes: Voice assistants processing commands locally avoid sending every conversation snippet to cloud servers, enhancing user privacy. [Related: Safeguarding Sanctuary: Smart Home Security & Privacy in the AI Era]
- Surveillance Systems: Facial recognition for access control can be performed on-site, ensuring that raw video feeds never leave the premises.
Reduced Bandwidth and Cost Savings
The sheer volume of data generated by modern IoT AI devices can overwhelm network infrastructure and incur substantial costs for data transmission. Edge AI dramatically reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud.
- Instead of streaming continuous high-definition video to the cloud, an
Edge AIcamera might only send metadata or event-triggered short clips. This leads toreduced bandwidth AI. - For a network of thousands of sensors,
AI processing on edgesignificantly lowers cloud storage and processing fees by pre-filtering and analyzing data locally before any relevant insights are transmitted. This makes large-scaledistributed AI computingmore economically viable.
Offline Capabilities and Robustness
Edge devices can function independently of a constant internet connection. This provides critical offline AI capabilities and enhances system robustness.
- In remote areas with unreliable connectivity, or during network outages,
AI on devicesystems can continue to operate and make intelligent decisions. - This is invaluable for applications in disaster zones, remote agricultural monitoring, or areas with intermittent satellite links, where continuous
AI at the network edgeis required.
Scalability and Efficiency
Deploying intelligence directly to devices allows for more scalable solutions. Instead of a centralized cloud server becoming a bottleneck for thousands or millions of devices, each smart device AI unit handles its own processing. This distributes the computational load, making the entire system more efficient and easier to scale. Managing the increasing number of IoT AI devices becomes more feasible when intelligence is decentralized AI.
A World of Applications: Where Edge AI is Making an Impact
The transformative power of Edge AI is manifesting across an incredible array of industries and everyday scenarios, bringing real-time intelligence to the forefront. These Edge AI use cases demonstrate the breadth of its potential.
Smart Homes and Personal Devices
Our homes are becoming smarter, and Edge AI is at the heart of this evolution.
- Voice Assistants: Modern smart speakers and smartphones use
AI on deviceto process common commands locally, speeding up response times and improvingprivacy preserving AI edge. - Smart Security Cameras: As mentioned earlier, cameras can perform
AI inference at the edgefor person detection, facial recognition, or package delivery alerts, sending only critical events to the user. - Home Appliances: Smart refrigerators could use
on-device machine learningto identify food items, track expiry dates, and suggest recipes without constant cloud communication. Edge AI for smart homesis making our living spaces more intuitive and responsive.
Autonomous Vehicles and Transportation
This is one of the most critical Edge AI applications, where low latency AI is a matter of life and death.
- Self-Driving Cars: Vehicles use
AI processing on edgeto interpret sensor data (cameras, lidar, radar) in real-time, identifying pedestrians, other vehicles, traffic signs, and road conditions instantly to navigate safely. - Drones: Autonomous drones for delivery or inspection use
Edge AIfor obstacle avoidance, target tracking, and precise navigation, even in areas with no network coverage. - Traffic Management:
Smart city edge AI applicationscan analyze traffic flow locally to optimize signal timings, reducing congestion and improving efficiency. This is vital forEdge AI for autonomous vehicles. [Related: AI Unleashed: Revolutionizing Space Exploration & Cosmic Discovery]

Manufacturing and Industrial IoT
Industry 4.0 relies heavily on IoT AI and Edge AI in manufacturing to enhance efficiency and safety.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors on machinery use
on-device machine learningto detect subtle anomalies that indicate impending failure, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing costly breakdowns. - Quality Control: High-speed cameras with
AI inference at the edgecan inspect products for defects on the assembly line in real-time, immediately flagging flawed items. - Worker Safety: Edge AI systems can monitor worker movements and detect potential hazards or violations of safety protocols.
Healthcare Innovations
Edge AI in healthcare is revolutionizing patient care, diagnostics, and monitoring.
- Wearable Health Monitors: Smartwatches and medical patches can continuously monitor vital signs, detect abnormal heart rhythms or falls, and process this data locally, alerting users or caregivers only when necessary.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Devices in a patient’s home can perform initial analysis of medical data, reducing the need for constant data transmission and improving
privacy preserving AI edge. - Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Portable medical imaging devices can use
AI on deviceto assist in preliminary diagnoses directly at the patient’s bedside or in remote clinics.
Retail and Smart Stores
Edge AI is transforming the retail experience.
- Inventory Management: Cameras and sensors can track shelf stock levels in real-time, alerting staff to replenish items.
- Customer Experience: Anonymous
Edge AIanalysis of foot traffic patterns helps optimize store layouts and product placement. - Loss Prevention: Intelligent security systems can identify suspicious behavior or unauthorized item removal instantly.
Agriculture
From crop monitoring to livestock management, IoT AI and Edge AI offer significant advantages.
- Precision Agriculture: Drones and ground sensors use
AI processing on edgeto analyze crop health, soil conditions, and pest infestations, enabling targeted irrigation and pesticide application. - Livestock Monitoring: Wearable sensors on animals can monitor health, detect illness, and track behavior patterns locally, alerting farmers to potential issues.
These are just a few examples of how Edge AI applications are reshaping our world, moving intelligence closer to the point of action and fostering a new era of responsiveness and efficiency.
Overcoming the Hurdles: Challenges in Edge AI Development
While the Edge AI benefits are numerous and compelling, the path to widespread adoption is not without its obstacles. Edge AI challenges require innovative solutions and careful consideration during Edge AI development.
Resource Constraints
Edge devices, by their nature, are often constrained in terms of processing power, memory, storage, and energy consumption.
- Power Efficiency: Many
IoT AIdevices are battery-powered, meaningAI processing on edgemust be extremely energy-efficient. This drives the demand for specialized hardware likeTinyMLchips. - Computational Limits: Running complex AI models on smaller processors without dedicated accelerators can be a significant challenge, requiring extensive model optimization.
- Memory Footprint: Large AI models demand substantial memory, which is often limited on edge devices.
Model Optimization and Deployment Complexity
Optimizing, deploying, and managing AI models across a diverse fleet of edge devices can be intricate.
- Heterogeneous Hardware: The vast array of different edge devices, each with unique hardware architectures and operating systems, makes universal model deployment difficult.
- Model Compression: Striking the right balance between model size, accuracy, and computational efficiency for
AI inference at the edgeis an ongoing research area. - Over-the-Air Updates: Reliably updating
AI on devicemodels and software for thousands or millions of geographically dispersed devices presents logistical and technical hurdles.
Security Vulnerabilities
While privacy preserving AI edge offers advantages, Edge AI security remains a critical concern.
- Physical Tampering: Edge devices are often deployed in accessible, unsecured environments, making them vulnerable to physical theft or tampering, which could expose models or data.
- Model Evasion/Poisoning: Adversarial attacks can fool
AI processing on edgemodels or even inject malicious data during training, compromising their integrity. - Secure Boot and Updates: Ensuring that only authorized and verified software runs on edge devices and that updates are secure is paramount.
Data Management and Integration
While Edge AI reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud, effective data orchestration between the edge and the cloud is still vital.
- Data Synchronization: Ensuring consistency between data processed at the edge and data stored or aggregated in the cloud can be complex.
- Model Retraining: Edge models often need to be periodically updated or retrained using new data collected from the edge. Efficient mechanisms for this feedback loop are essential.
- Orchestration: Managing the lifecycle of thousands of
decentralized AImodels, from deployment to monitoring and retirement, requires robust orchestration tools.
Addressing these Edge AI challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving hardware innovation, advanced software tools, robust security protocols, and intelligent data management strategies.
The Road Ahead: The Future of Edge AI
The trajectory of Edge AI is steep and accelerating, promising a future where intelligence is ubiquitous, responsive, and deeply integrated into our physical world. Several key trends are shaping the future of Edge AI.
Ubiquitous Intelligence and Hyper-Personalization
As AI on device capabilities become more powerful and efficient, every device, from tiny sensors to powerful industrial robots, will possess inherent intelligence. This will lead to hyper-personalized experiences, with devices adapting to individual needs and contexts without needing constant cloud interaction. Imagine smart glasses providing real-time information overlays, or hearing aids filtering specific sounds based on your environment, all powered by AI processing on edge.
Convergence with 5G and IoT
The widespread rollout of 5G networks, with their ultra-low latency and massive connectivity, will supercharge IoT AI and Edge AI. 5G will provide the high-speed, reliable communication backbone needed to connect vast numbers of edge devices to each other and to the cloud, forming a seamless intelligent fabric. The synergy between AI at the network edge and reduced bandwidth AI capabilities of 5G will unlock new Edge AI applications that are currently unimaginable. [Related: Web3 Creator Economy: Empowering Artists & Innovators]
Advances in TinyML
The field of TinyML will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible on highly constrained devices. Further research into ultra-low-power AI chips, highly compressed models, and efficient inference algorithms will enable on-device machine learning to be embedded into even smaller, more energy-efficient form factors, expanding the reach of Edge AI into new domains.
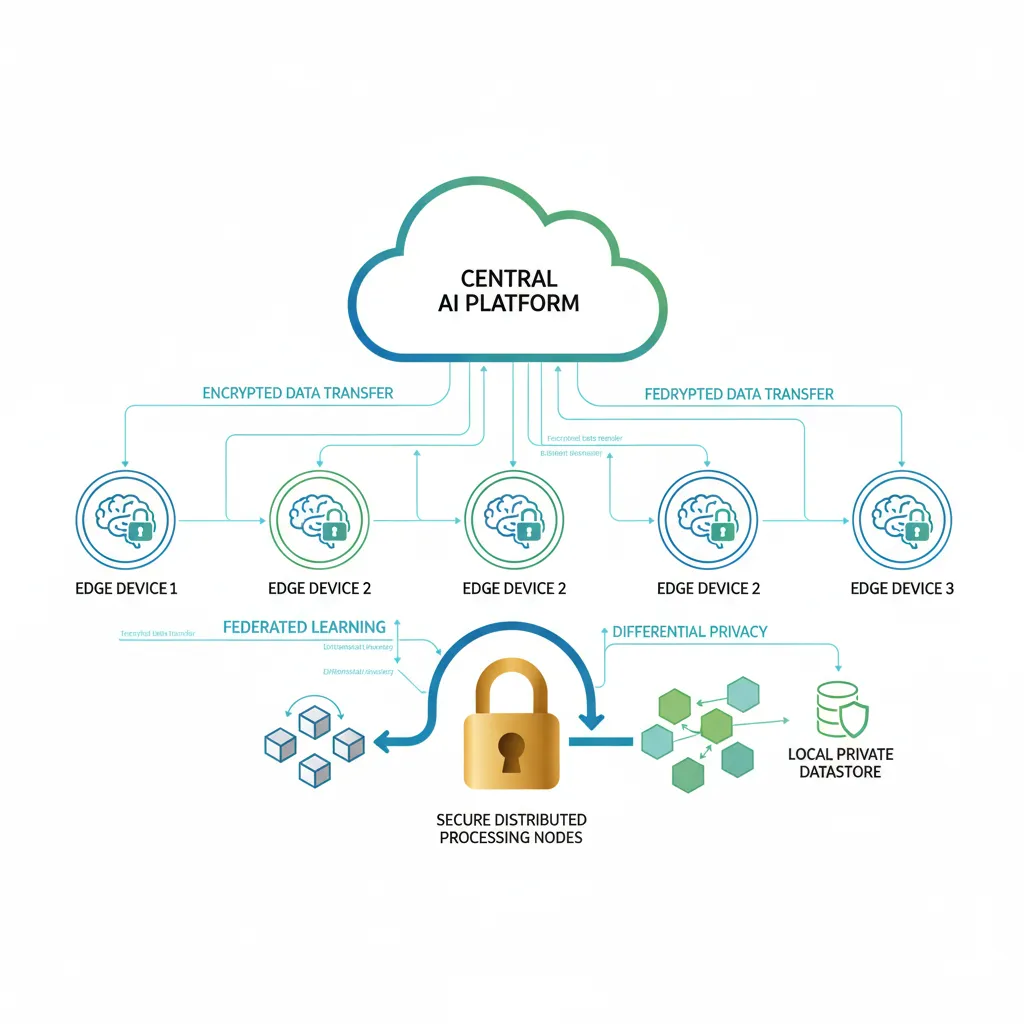
Federated Learning and Collaborative AI
Federated learning edge AI is set to become a cornerstone of privacy-preserving and collaborative AI. In federated learning, models are trained collaboratively across multiple AI processing on edge devices, each retaining its local data. Only aggregated model updates (not raw data) are sent to a central server, significantly enhancing privacy preserving AI edge while improving overall model accuracy. This decentralized AI approach is perfect for scenarios involving sensitive data like healthcare records or personal user behavior.
Edge AI Market Trends and Investment
The Edge AI market trends indicate substantial growth, with increasing investment from tech giants, startups, and venture capitalists. Industries across the board are recognizing the strategic importance of Edge AI development for competitive advantage, driving demand for specialized hardware, software platforms, and skilled professionals. We’ll see more Edge AI use cases emerging as the technology matures.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
As Edge AI becomes more pervasive, regulatory bodies and society at large will grapple with ethical considerations. Questions around data ownership, algorithmic bias in AI on device models, accountability for autonomous real-time AI decisions, and the responsible use of AI at the network edge will become increasingly important. Proactive development of ethical AI guidelines and robust regulatory frameworks will be crucial.
The future of Edge AI promises a world where intelligent systems are not just faster and more efficient, but also more private, robust, and deeply embedded in the fabric of our existence. It’s an exciting frontier that will continue to redefine our relationship with technology.
Conclusion
Edge AI represents a pivotal shift in the landscape of artificial intelligence, moving the frontier of intelligence from centralized cloud servers to the very devices and points where data is generated and actions are taken. This paradigm of decentralized AI empowers smart device AI with real-time intelligence, enabling everything from autonomous vehicles that make split-second decisions to smart homes that anticipate our needs with enhanced privacy.
We’ve explored how AI on device thrives on specialized hardware and optimized models, delivering profound Edge AI benefits like low latency AI, reduced bandwidth AI, and critical offline AI capabilities. From transforming Edge AI in manufacturing and Edge AI in healthcare to revolutionizing Edge AI for autonomous vehicles and Edge AI for smart homes, its Edge AI applications are as diverse as they are impactful.
While Edge AI challenges such as resource constraints, model deployment complexities, and Edge AI security require ongoing innovation, the future of Edge AI is undeniably bright. With advancements in TinyML, the rise of federated learning edge AI, and the convergence with 5G and IoT AI, AI at the network edge is poised to create a world that is not just smarter, but also more responsive, secure, and profoundly intelligent. Embrace the edge – it’s where the next wave of innovation is truly happening.
FAQs
Q1. What is Edge AI?
Edge AI refers to the deployment of artificial intelligence algorithms and machine learning models directly on local devices or servers at the “edge” of a network, enabling data processing and decision-making closer to the source of data generation rather than relying on centralized cloud infrastructure. It’s about bringing AI on device.
Q2. How is Edge AI different from cloud AI?
Cloud AI processes data in remote, centralized data centers, requiring data transmission over networks. Edge AI, conversely, processes data locally on the device itself or nearby edge servers. This distinction leads to low latency AI, enhanced privacy preserving AI edge, and reduced bandwidth AI for Edge AI, while cloud AI offers immense processing power for large-scale training and complex tasks.
Q3. What are some examples of Edge AI in everyday life?
Common examples include voice assistants on smartphones (processing commands locally), smart security cameras performing AI inference at the edge for person detection, facial recognition in modern phones, and predictive text on your keyboard. Edge AI for smart homes devices also use this technology.
Q4. What are the main benefits of Edge AI?
The primary Edge AI benefits include real-time AI processing (due to low latency AI), improved data privacy preserving AI edge and security (as data stays local), reduced bandwidth AI usage (less data sent to the cloud), offline AI capabilities (functionality without constant internet), and enhanced system robustness and scalability.
Q5. What challenges does Edge AI face?
Key Edge AI challenges include the limited processing power, memory, and energy constraints of edge devices; the complexity of Edge AI development and optimizing large AI models for these constraints; and ensuring robust Edge AI security against physical tampering or adversarial attacks in distributed environments.
Q6. What is TinyML?
TinyML is a specialized field within Edge AI focused on performing on-device machine learning on extremely low-power, resource-constrained microcontrollers and embedded devices. It enables AI capabilities in tiny sensors and wearables where power and memory are severely limited.
Q7. Is Edge AI more secure than cloud AI?
Edge AI can offer enhanced security and privacy preserving AI edge for specific use cases because sensitive raw data doesn’t always need to leave the local device or network. However, edge devices themselves can be vulnerable to physical tampering or cyberattacks, so robust Edge AI security measures are still crucial. It shifts some security considerations from network transmission to device-level protection.
Q8. What is federated learning in the context of Edge AI?
Federated learning edge AI is a decentralized AI approach that allows multiple edge devices to collaboratively train a shared machine learning model without directly sharing their raw data. Instead, each device trains a local model and sends only aggregated model updates (weights or gradients) to a central server, which then combines these updates to improve the global model. This significantly enhances privacy preserving AI edge.