AI Unleashed: Accelerating Cosmic Discoveries & Space Missions
Introduction
The universe is whispering its secrets, but it speaks in a language of immense, overwhelming data. For centuries, our ability to listen has been limited by our own human capacity. Telescopes, probes, and satellites send back petabytes of information—a cosmic flood that would take lifetimes to sift through manually. But what if we had a partner in this grand quest for knowledge? A partner that could see patterns in stellar light that we can’t, navigate alien worlds with inhuman precision, and manage our orbital assets with flawless logic. This is no longer science fiction; it’s the new reality of AI space exploration.
Artificial intelligence is rapidly becoming the indispensable co-pilot for humanity’s journey into the final frontier. From the red dust of Mars to the farthest reaches of our galaxy, artificial intelligence in space is transforming how we conduct missions, analyze findings, and make groundbreaking discoveries. This article delves into how AI for space missions is not just an upgrade but a complete paradigm shift. We’ll explore how space discovery AI is decoding cosmic mysteries, powering autonomous robots, and paving the way for the ambitious future of space exploration AI. Get ready to see how algorithms are becoming as crucial as rockets in our quest to understand the cosmos.
The New Co-Pilot: How AI is Redefining Space Exploration
At its core, the greatest challenge in modern astronomy is the sheer scale of data. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), for instance, can generate over 200 gigabits of data per day. Sifting through this digital deluge for a single, meaningful signal—like the atmospheric composition of a distant exoplanet—is like finding a specific grain of sand on a global beach.
This is where machine learning space science comes into play. Instead of programming a computer with explicit instructions on what to find, we train algorithms on vast datasets, teaching them to recognize patterns, anomalies, and objects of interest on their own. Deep learning space imagery techniques, which use complex neural networks inspired by the human brain, are particularly powerful. They can classify galaxies, identify supernovae, and flag potential phenomena for human astronomers to investigate further.
Think of AI as a tireless research assistant with superhuman pattern recognition. It doesn’t get bored or fatigued. It can analyze the light curves of a million stars simultaneously, something no team of humans could ever achieve. This frees up scientists to focus on higher-level analysis, interpretation, and theoretical work, dramatically accelerating the pace of AI driven space research.
Related: The Rise of AI Personal Assistants: Automate Your Life & Boost Productivity
From Data to Discovery: AI’s Role in Unveiling Cosmic Secrets
The primary application of AI in space is turning raw, incomprehensible data into profound scientific discoveries. It acts as a universal translator for the cosmos, revealing insights hidden within the noise.
Hunting for New Worlds: AI-Powered Exoplanet Detection
Before AI, finding exoplanets—planets orbiting other stars—was a painstaking process. The “transit method,” which looks for tiny, periodic dips in a star’s brightness as a planet passes in front of it, often produces false positives from sunspots or instrument errors.
Now, AI exoplanet detection algorithms are a game-changer. Scientists at NASA and other institutions train neural networks on confirmed planet transit data from telescopes like Kepler and TESS. The AI learns the subtle signature of a true exoplanet and can then scan new datasets with incredible speed and accuracy. In 2017, Google’s AI helped discover Kepler-90i, the eighth planet in a distant solar system, by analyzing old data that had been previously overlooked. This confirmed that other solar systems could be just as crowded as our own, a discovery made possible by AI planetary discovery tools.
Decoding the Universe’s Language: AI Data Analysis in Space
Beyond finding new worlds, AI data analysis space tools are being applied across the entire field of astrophysics. These cosmic discovery AI tools are essential for making sense of the universe’s complexity.

Applications include:
- Galaxy Classification: Deep learning models can categorize millions of galaxies by shape (spiral, elliptical, irregular) in mere hours, a task that once took years of manual labor through citizen science projects like Galaxy Zoo.
- Gravitational Lensing: AI can identify instances of gravitational lensing, where the gravity of a massive foreground object bends the light from a distant one. This helps astronomers map the distribution of dark matter in the universe.
- Detecting Cosmic Events: AI algorithms constantly monitor telescope feeds to spot transient events like supernovae or kilonovae—the explosive mergers of neutron stars. This AI for cosmic events gives astronomers an early warning to point other instruments at the phenomenon to capture crucial data.
The Unseen Threat: AI Asteroid Tracking and Planetary Defense
The solar system is a cosmic shooting gallery, and Earth is not immune. Identifying and tracking Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) is critical for planetary defense. The challenge is spotting small, fast-moving, and often dim objects against a backdrop of millions of stars.
AI asteroid tracking systems are our new sentinels. Algorithms powered by machine learning can analyze images from sky surveys like Pan-STARRS and the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory much faster than humans. They can differentiate between a new asteroid and a satellite or image artifact, calculate its trajectory, and flag it for potential impact risk. This automated process is crucial for providing the lead time necessary to plan a mitigation mission, should a hazardous object be found on a collision course with Earth.
Intelligent Machines in the Final Frontier: Robotics and Autonomy
While AI is revolutionizing how we see the universe, it’s also changing how we physically explore it. The vast distances and communication delays in space make direct real-time control of robotic explorers impossible. Autonomy is not a luxury; it’s a necessity.
Smarter Rovers, Bolder Missions: AI for Martian Exploration
When you send a command to a Mars rover, it can take anywhere from 4 to 24 minutes for the signal to arrive. This communication lag means rovers can’t be “driven” like remote-controlled cars. They need to think for themselves.
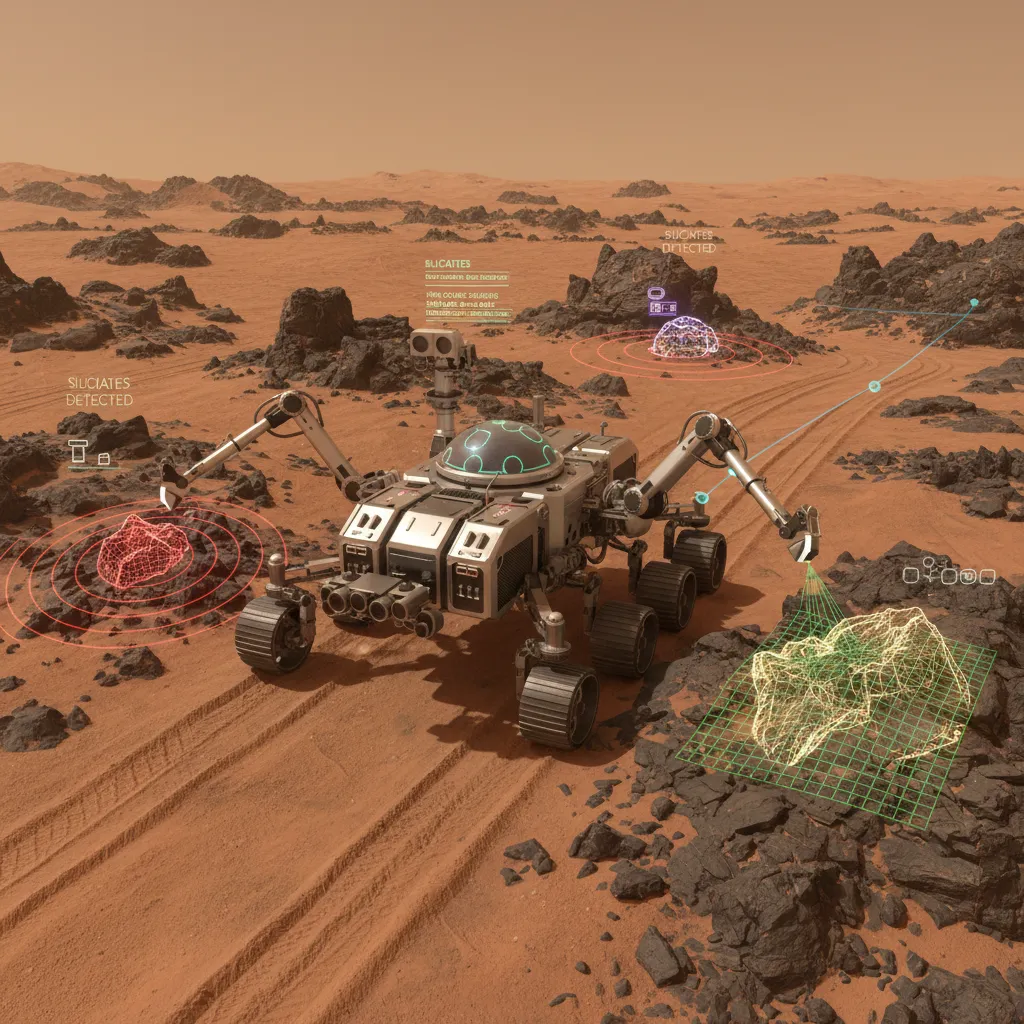

This is where autonomous spacecraft AI shines. NASA’s Perseverance and Curiosity rovers use sophisticated AI for navigation and science.
- AutoNav: This system uses stereo camera images to build a 3D map of the surrounding terrain, identify hazards like large rocks or steep slopes, and plot the safest and most efficient path forward. This allows the rover to cover more ground and explore areas that would be too risky under direct human planning.
- AEGIS (Autonomous Exploration for Gathering Increased Science): This is one of the most exciting examples of AI for Martian missions. AEGIS uses machine learning to analyze images from the rover’s cameras and identify geological features of high scientific interest, such as specific types of rocks or soil textures. It can then autonomously aim and fire its laser spectrometer to analyze the target’s chemical composition without waiting for instructions from Earth. This space robotics AI allows for opportunistic science, ensuring no discovery is missed.
The Orbital Choreographers: AI for Satellite Operations and Debris Management
Our planet is surrounded by a cloud of thousands of active satellites, crucial for communication, navigation, weather forecasting, and more. Managing these complex constellations is a monumental task. AI for satellite operations is becoming the master choreographer of this orbital ballet. AI systems can:
- Optimize Orbits: Automatically adjust satellite trajectories to conserve fuel and maintain optimal positioning.
- Predict Failures: Monitor telemetry data to predict component failures before they happen, allowing for preventative measures.
- Manage Bandwidth: Intelligently allocate communication bandwidth across a constellation to meet demand in real-time.
An even greater challenge is the growing threat of space junk. Decades of launches have left millions of pieces of debris in orbit, traveling at hypersonic speeds. A collision with even a small piece can be catastrophic. AI space debris management uses machine learning to track these objects, predict their orbital paths with greater accuracy, and automatically calculate collision avoidance maneuvers for active satellites and the International Space Station.
Related: Sustainable Finance: How to Invest Responsibly & Grow a Green Portfolio
The Resource Rush: AI in Space Mining and Resource Utilization
Looking further ahead, the concept of utilizing resources found in space—on the Moon, Mars, or asteroids—is becoming a serious goal. Space mining AI will be essential for making this a reality.

Prospecting missions will use AI space resources algorithms to analyze sensor data and identify asteroids or lunar regions rich in water ice, metals, or other valuable materials. Once a target is selected, swarms of autonomous mining robots, coordinated by a central AI, will be needed to extract and process these resources without constant human supervision.
The Human Element: AI as a Partner for Astronauts and Mission Control
AI’s role isn’t just about data and robots; it’s also about augmenting and protecting the human pioneers of space. For long-duration missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, AI will be a critical crewmate.
The Ultimate Assistant: AI for Astronaut Support
Life in a space habitat is a high-stakes, high-stress environment. AI for astronaut assistance aims to reduce cognitive load and enhance safety. An onboard AI could function as an intelligent assistant, much like CIMON (Crew Interactive Mobile Companion), an AI-powered helper tested on the ISS.

This digital crewmate could:
- Manage complex procedures by providing voice-prompted instructions and visual aids.
- Monitor life support systems and vehicle health, providing early warnings of anomalies (AI space environment monitoring).
- Track crew health vitals and even offer preliminary diagnostic support.
- Help manage inventory, schedules, and scientific experiments.
Optimizing the Journey: AI in Space Mission Planning and Communication
Every space mission is a puzzle of immense complexity, balancing fuel, time, and risk. AI space mission planning is used to solve this puzzle. AI can run millions of simulations to calculate the most efficient trajectories for interplanetary travel, optimizing for factors like launch windows and gravity assists.
Communication across the vastness of space is another challenge. AI deep space communication is being developed to tackle this. AI algorithms can help clean up degraded signals, compress data more efficiently to transmit more science back to Earth, and intelligently manage communication schedules between multiple missions and the Deep Space Network.
Related: Mind Meld: The Rise of Neurotech and Brain-Computer Interfaces
The Future is Now: Next-Generation AI in Space
We are only at the beginning of the AI revolution in space. The convergence of more powerful computing, sophisticated algorithms, and ambitious mission goals promises a future of even more incredible possibilities.
Intelligent space systems are the next frontier. Imagine a mission that can design and execute its own scientific campaign. A probe arriving at Jupiter’s moon Europa, for example, could use AI to identify a promising region, deploy a lander, drill through the ice, and analyze the subsurface ocean for signs of life—all without step-by-step commands from Mission Control. This is the goal of next gen space tech AI.
Smart telescopes AI will integrate artificial intelligence directly into the hardware, allowing them to autonomously identify and track interesting targets. And the search for life itself will be supercharged by AI in astrobiology, where algorithms will scan the atmospheric data of thousands of exoplanets for the tell-tale chemical fingerprints—or biosignatures—of life.
Conclusion
From sifting through the light of distant stars to guiding rovers across alien landscapes, artificial intelligence has fundamentally transformed our relationship with the cosmos. It is no longer just a tool but a foundational partner, accelerating the pace of discovery, enabling missions of unprecedented autonomy, and ensuring the safety of our explorers. The immense challenges of data overload, communication delays, and operational complexity are being met by the power of AI space exploration.
As we stand on the precipice of a new golden age of discovery—returning to the Moon, setting our sights on Mars, and peering deeper into the universe than ever before—AI will be at the helm. It is the key that will unlock the answers to our oldest questions: Are we alone? How did the universe begin? And what is our place within it? The journey is just beginning, and with AI as our co-pilot, the possibilities are as limitless as space itself.
What AI-driven space mission or discovery are you most excited to see in the future? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How is artificial intelligence used in space exploration?
Artificial intelligence is used in a wide array of applications, including analyzing massive datasets from telescopes to find exoplanets and classify galaxies, navigating rovers autonomously on planets like Mars, managing complex satellite operations, tracking potentially hazardous space debris, and assisting astronauts with tasks on the International Space Station.
What is the role of AI in NASA’s missions?
NASA leverages AI across numerous missions. A key example is the AEGIS system on the Mars Perseverance rover, which uses AI to autonomously select and analyze rock targets. AI is also critical for processing the vast amounts of data from the James Webb and Hubble Space Telescopes and for planning optimal trajectories for deep space missions.
Can AI discover new planets?
Yes, absolutely. AI, specifically machine learning algorithms, has been instrumental in discovering thousands of new exoplanets. It excels at analyzing data from telescopes like Kepler and TESS, identifying the incredibly subtle and periodic dips in starlight that indicate a planet is passing in front of its star, a task where AI often outperforms human analysis in both speed and accuracy.
How does AI help with space debris?
AI helps manage the critical problem of space debris by using machine learning models to predict the complex orbits of millions of debris fragments. These AI space debris management systems can accurately calculate the risk of a potential collision with active satellites or crewed spacecraft and automatically recommend or execute avoidance maneuvers.
What is an example of an AI robot in space?
A prime example of an AI space robotics system is NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover. It uses an AI-powered navigation system called AutoNav to autonomously drive and avoid obstacles on the Martian surface. Its AEGIS system also uses AI to identify scientifically interesting targets and perform analysis without waiting for commands from Earth.
How will AI shape the future of space travel?
In the future, AI will be even more integral. It will enable fully autonomous science missions to the outer planets, manage fleets of spacecraft for space mining AI, help construct and maintain off-world habitats, and power smart telescopes AI. Furthermore, AI in astrobiology will play a key role in analyzing atmospheric data from exoplanets in the search for signs of extraterrestrial life.