AI Revolutionizes Early Disease Detection: A Lifesaving Leap in Healthcare

For centuries, medicine has largely operated on a reactive model: you feel sick, you see a doctor, you get a diagnosis, and you start treatment. But what if we could flip the script? What if we could find the whispers of disease long before they become a roar? This is no longer science fiction; it’s the reality being built today, powered by Artificial Intelligence. The integration of AI disease detection is ushering in an era of proactive, predictive, and personalized healthcare, marking one of the most significant AI in healthcare advancements of our time.
The challenge with many of the world’s deadliest diseases—cancer, heart disease, neurodegenerative disorders—is that they are often silent in their early stages. By the time symptoms appear, the window for most effective treatment may have narrowed. This is where early disease diagnosis AI comes in, acting as a tireless, microscopic detective. It sifts through mountains of data, from medical scans to genetic code, to find subtle patterns that would be invisible to the human eye.
In this deep dive, we’ll explore the groundbreaking ways AI is revolutionizing diagnostics. We’ll examine how predictive analytics healthcare is forecasting illness, how AI medical imaging is spotting cancer with superhuman accuracy, and what the future of diagnostics AI holds for us all. This is more than just a health tech innovation; it’s a lifesaving leap that promises to improve AI patient outcomes and redefine our relationship with health itself.
The Paradigm Shift: From Reactive Treatment to Proactive Prevention
The traditional healthcare journey is familiar. It’s a path of appointments, tests, and treatments that begins once a health problem has already taken root. AI in preventive medicine is fundamentally altering this journey. It’s about shifting the focus from treating sickness to preserving wellness.
Imagine a system that continuously monitors for risks, flags potential issues years in advance, and provides personalized recommendations to keep you healthy. This is the core promise of an AI driven health ecosystem. Instead of waiting for a tumor to grow large enough to be felt or for a cardiac event to occur, AI models can analyze risk factors, lifestyle data, and biomarkers to calculate a person’s probability of developing a specific condition.
This proactive stance is made possible by machine learning’s ability to process and learn from datasets of a scale unimaginable just a decade ago. These systems can correlate thousands of variables to create highly accurate predictive models, forming the backbone of smart healthcare solutions that empower both patients and clinicians.
The Core Engine: How Machine Learning Sees the Unseen
At the heart of this revolution are machine learning (ML) and deep learning, a subset of ML. These algorithms are trained on vast quantities of medical data, learning to recognize the intricate signatures of various diseases. They don’t just follow programmed instructions; they learn, adapt, and improve their diagnostic accuracy AI over time.
Seeing the Unseen: AI in Medical Imaging and Radiology
One of the most mature and impactful applications of AI is in medical imaging. Radiologists and pathologists spend their careers training their eyes to spot abnormalities in MRIs, CT scans, X-rays, and tissue slides. It’s a skill that requires immense expertise, yet even the best experts can face challenges with fatigue, overwhelming caseloads, and the sheer subtlety of early-stage disease markers.

This is where deep learning medical diagnosis shines. A type of algorithm called a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), inspired by the human visual cortex, can be trained on millions of medical images.
- Early Cancer Detection: In oncology, AI for cancer detection is a game-changer. AI algorithms can highlight suspicious regions on a mammogram that may indicate early breast cancer, detect tiny lung nodules on a CT scan that could be malignant, or analyze skin lesions for signs of melanoma with incredible precision. This field of early cancer detection AI is dramatically increasing the chances of successful treatment.
- AI Radiology: AI doesn’t just spot anomalies; it can also quantify them. For instance, it can measure the exact size and growth rate of a tumor over time, providing objective data for treatment planning. It streamlines the workflow for radiologists, prioritizing critical cases and reducing the time from scan to diagnosis. [Related: GPT-4o: The AI That Hears, Sees, and Speaks - An Omnidirectional Model]
- Neurology and Cardiology: Beyond cancer, AI medical imaging is used to detect signs of stroke, identify brain aneurysms, and assess heart function from echocardiograms, often faster and more consistently than human analysis alone.
These AI-powered diagnostics act as a second pair of expert eyes, augmenting the skills of clinicians and catching what might have otherwise been missed.
Decoding Our Blueprint: AI in Genomics and Biomarker Discovery
Our DNA holds the blueprint for our health, but it’s an incredibly complex language. Analyzing the 3 billion base pairs of the human genome for disease-causing mutations is a monumental task. AI and health data analytics AI are making it possible.

AI algorithms can rapidly scan genetic data from thousands of individuals, identifying novel gene sequences and biomarkers associated with diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and various cancers. By understanding the genetic underpinnings of a disease, we can:
- Assess Risk: Identify individuals with a high genetic predisposition to certain conditions long before symptoms emerge.
- Enable Precision Health: Move towards personalized medicine AI, where treatments are tailored to a patient’s unique genetic profile. This ensures therapies are more effective and have fewer side effects.
- Discover New Drug Targets: By pinpointing the specific biological pathways a disease affects, AI and biomarkers research can accelerate the development of new, targeted drugs. This fusion of genomics and AI is the cornerstone of AI precision health.
Beyond the Image: Predictive Analytics and Real-Time Monitoring
While imaging and genomics look at static snapshots of our health, predictive analytics healthcare models analyze dynamic, longitudinal data to forecast future health events. This is where AI moves from a diagnostic tool to a prognostic one.
Predicting the Future: AI in Cardiology, Diabetes, and Chronic Disease
Chronic diseases account for the vast majority of healthcare costs and mortality worldwide. AI for chronic disease management offers a powerful solution for early intervention.
- AI in Cardiology: By analyzing a patient’s electronic health record (EHR), ECG results, and even data from wearables like smartwatches, AI models can predict the 5-year or 10-year risk of a heart attack or stroke with high accuracy. Google’s AI, for example, has shown it can predict cardiovascular risk factors simply by analyzing retinal scans—a non-invasive and powerful screening tool.
- AI for Diabetes Prediction: Machine learning can identify individuals at high risk for developing Type 2 diabetes by analyzing factors like age, BMI, family history, and blood test results. This allows for targeted lifestyle interventions (diet, exercise) that can prevent or delay the onset of the disease entirely, representing a major step forward in real-time disease detection and prevention. [Related: The Rise of Small Language Models: Powering the Edge AI Revolution]
Smart Health Screening: Making Prevention Accessible and Efficient
The success of any preventive strategy hinges on effective screening. However, population-wide screening can be expensive and logistically complex. AI health screening technologies are making these programs more efficient, affordable, and patient-friendly.

AI can optimize screening schedules, automate the initial analysis of results, and even power portable, low-cost diagnostic devices that can be deployed in remote or underserved communities. This democratization of diagnostics is a critical step in reducing health disparities and one of the most promising healthcare technology trends.
The Real-World Impact: AI Diagnostics in Action
These medical AI breakthroughs are not just theoretical; they are being deployed in clinics and hospitals worldwide. Companies like Viz.ai have FDA-cleared AI that analyzes brain scans to detect signs of stroke and alerts specialists in minutes, drastically cutting down treatment time. Others, like PathAI, provide AI-powered pathology tools that assist in cancer diagnosis, improving accuracy and consistency.
The impact on the diagnostic timeline is profound. What once took days or weeks of analysis and consultation can now often be done in minutes.
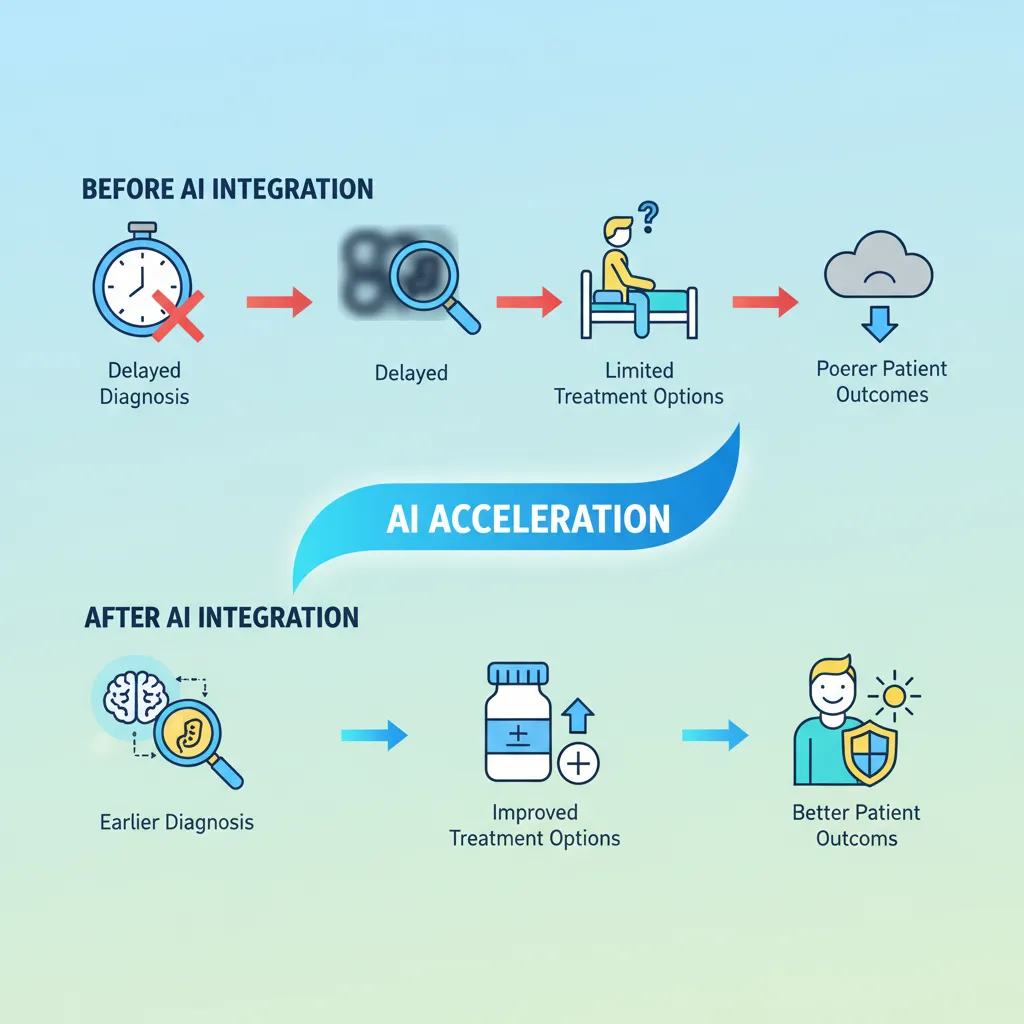
This acceleration doesn’t just reduce patient anxiety; it directly translates to better AI patient outcomes. For aggressive diseases, every day counts, and AI is giving patients and doctors more of them. [Related: Human-AI Synergy: The Future of Work and Productivity]
Navigating the New Frontier: Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As with any transformative technology, the rise of machine learning disease diagnosis comes with significant challenges and ethical questions that must be addressed responsibly.
- The “Black Box” Problem: Some complex deep learning models can be “black boxes,” meaning even their creators don’t fully understand how they arrive at a specific conclusion. For high-stakes medical decisions, this lack of transparency is a major concern.
- Data Bias: AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. If training data is not diverse and representative of the global population, the resulting algorithms can perpetuate and even amplify existing health disparities.
- Data Privacy and Security: Medical data is incredibly sensitive. Ensuring the robust security and privacy of patient information used to train and run AI models is paramount.
- Regulation and Accountability: Who is responsible when an AI makes a diagnostic error? Establishing clear regulatory frameworks (like those from the FDA) and lines of accountability is crucial for safe implementation.
Addressing these issues is at the forefront of ethical AI in medicine. The goal is not for AI to replace clinicians but to create a synergy where technology handles the data-intensive analysis, freeing up doctors to focus on what they do best: patient care, complex decision-making, and empathy. [Related: Google’s Project Astra: The Future of AI as a Universal Agent]
The Road Ahead: The Future of Diagnostics AI
We are still in the early innings of the AI in healthcare advancements. The future of diagnostics AI is pointing towards a world of continuous, passive, and deeply personalized health monitoring.
Imagine smart home devices that analyze your voice for early signs of cognitive decline, wearables that monitor your sweat for biomarkers, and AI agents that synthesize all this data into a real-time health dashboard for you and your doctor. This is the vision of proactive, ubiquitous, and democratized healthcare.
The journey will require continued innovation, rigorous validation, and a steadfast commitment to ethical principles. But the potential is undeniable.
Conclusion: A Healthier Tomorrow, Today
The integration of artificial intelligence into early disease detection is not an incremental improvement; it is a fundamental transformation of healthcare. From the enhanced vision of AI radiology to the predictive power of health data analytics AI, these tools are empowering us to confront disease on our own terms—proactively and preemptively.
We are witnessing the birth of a new era in medicine, one where medical AI breakthroughs save lives not by curing advanced disease, but by preventing it from ever taking hold. The fusion of human expertise and artificial intelligence promises a future where “early detection” means identifying risk at the molecular level, creating a healthier, more hopeful tomorrow for everyone. The journey of AI driven health has just begun, and its potential is truly lifesaving.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is AI used for early disease detection?
AI is used for early disease detection by training algorithms on massive datasets of medical information, such as images, genetic data, and electronic health records. These models learn to identify subtle patterns and biomarkers that are often invisible to the human eye, allowing them to flag potential diseases like cancer, heart disease, or diabetes at their earliest, most treatable stages.
Q2. What are some examples of AI diagnosing diseases?
Key examples include AI medical imaging for radiology, where algorithms analyze CT scans and MRIs to spot tumors or signs of stroke. In dermatology, AI can analyze photos of skin lesions to detect melanoma. Additionally, AI in cardiology uses ECG data to predict cardiac events, and predictive analytics healthcare models scan patient records to forecast the risk of chronic conditions.
Q3. Can AI predict health problems?
Yes, a major strength of AI in healthcare is its predictive capability. By analyzing a combination of genetic information, lifestyle data, and clinical history, machine learning disease diagnosis models can calculate an individual’s risk of developing specific health problems in the future. This allows for proactive interventions and personalized preventive care.
Q4. What are the limitations of using AI in diagnostics?
The main limitations include the potential for bias in algorithms if trained on non-diverse data, the “black box” nature of some models where the reasoning isn’t clear, and significant concerns around data privacy and security. Furthermore, AI systems require rigorous validation and regulatory approval, and their performance can vary depending on the clinical setting.
Q5. Will AI replace doctors in the future?
It is highly unlikely that AI will replace doctors. The consensus among experts is that AI will serve as a powerful tool to augment human clinicians, not replace them. AI excels at data analysis and pattern recognition, while doctors provide critical thinking, empathy, and complex decision-making. The future is a collaborative model of human-AI synergy to improve AI patient outcomes.
Q6. How does machine learning work in disease diagnosis?
In disease diagnosis, machine learning algorithms are “trained” by being fed vast amounts of labeled data (e.g., thousands of medical scans labeled as “cancerous” or “benign”). The algorithm learns the features associated with each label. Once trained, it can analyze new, unlabeled data and make a highly accurate prediction or classification, such as identifying a tumor in a new scan.
Q7. What is the impact of AI on patient outcomes?
The impact is overwhelmingly positive. By enabling earlier and more accurate diagnoses, AI leads to faster treatment, which significantly improves survival rates and quality of life for many diseases. AI for chronic disease management helps prevent complications, and personalized medicine AI ensures patients receive the most effective treatments for their specific condition, ultimately leading to better overall health outcomes.