AI’s Precision Revolution: Targeting Drugs for a Healthier Future

Introduction
For decades, the journey of creating a new medicine has been a marathon of epic proportions—a costly, time-consuming, and often frustrating process. Imagine searching for a single, unique key to fit a complex, changing lock, but your warehouse contains billions of nearly identical keys. This has been the reality of drug development. The “one-size-fits-all” approach, while groundbreaking in its time, often means that a drug effective for one person might be useless or even harmful to another.
But what if we could build the perfect key from scratch, tailored specifically for each lock?
This is the promise of the precision revolution, a paradigm shift in medicine powered by artificial intelligence in healthcare. We’re moving away from blockbuster drugs for the masses and into an era of personalized drug therapy and patient-specific treatments. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the new reality of AI drug discovery, where algorithms are achieving in weeks what used to take scientists years.
In this deep dive, we’ll explore how the convergence of big data, genomics, and machine learning is dismantling the old pharmaceutical model. We will uncover how AI in pharmacology is not just making drug development faster and cheaper but fundamentally more intelligent, leading to safer, more effective treatments and a healthier future for everyone.
The Billion-Dollar Problem: Why Traditional Drug Development Was Ripe for Disruption
Before we can appreciate the magnitude of the AI pharmaceutical innovation, it’s crucial to understand the system it’s revolutionizing. The traditional drug development pipeline has been the backbone of modern medicine, but it’s a process fraught with inefficiency and staggering costs.
Here’s a quick snapshot of the old way:
- Discovery (3-6 years): Scientists spend years in the lab trying to understand a disease at a molecular level to identify a “target”—like a specific protein or gene involved in the disease process.
- Preclinical Research (1-2 years): They then screen thousands, sometimes millions, of chemical compounds to find one that might interact with this target. This is followed by extensive testing in cells and animals.
- Clinical Trials (6-7 years): If a compound looks promising, it moves to human testing, a three-phase process that is incredibly expensive and has a shockingly high failure rate.
- FDA Review & Approval (1-2 years): After all that, regulatory bodies meticulously review the data before the drug can reach the market.
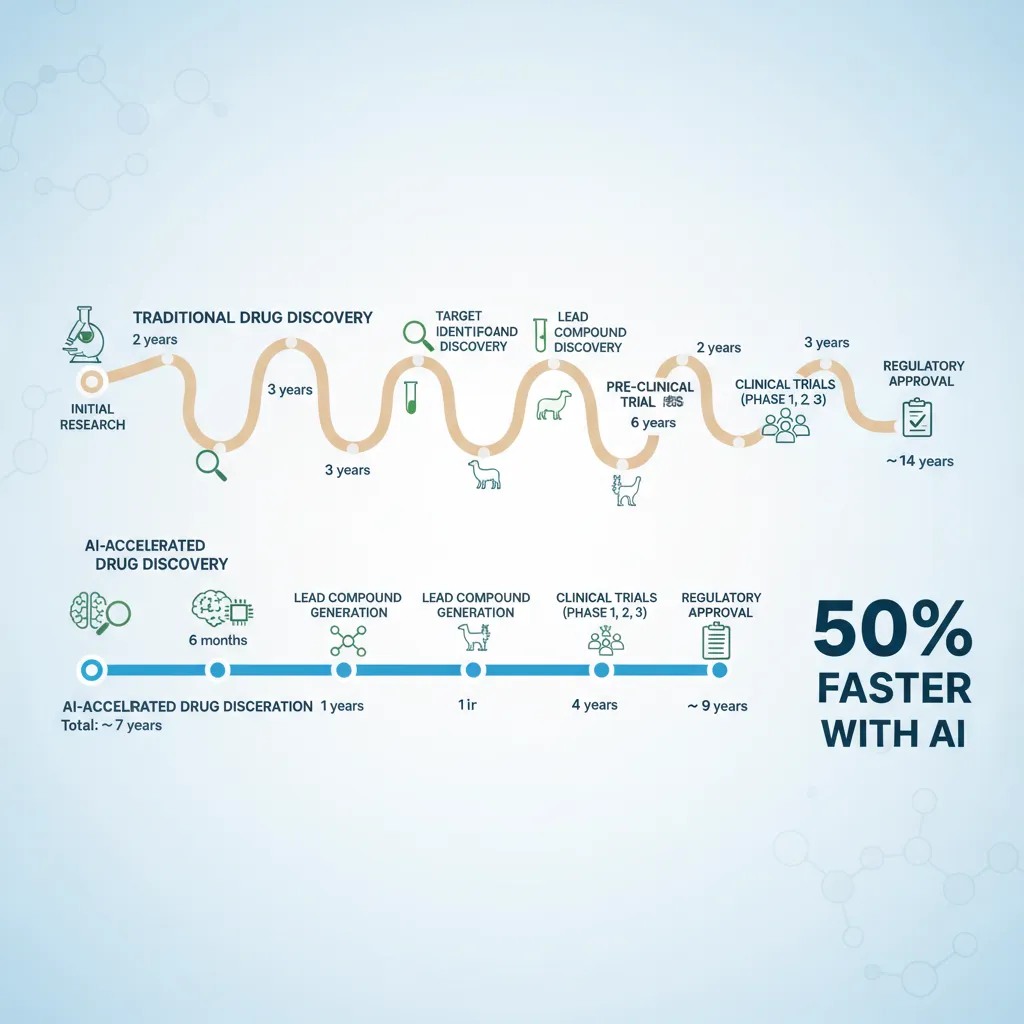
The result? It takes an average of 10 to 15 years and costs upwards of $2.6 billion to bring a single new drug to patients. Worse yet, over 90% of drugs that enter clinical trials fail to get approved. This broken model stifles innovation, keeps life-saving treatments from patients who need them, and contributes to skyrocketing healthcare costs. The core issue has always been a lack of precision—we were using a shotgun when we needed a laser-guided missile.
Enter the AI Architect: Rebuilding the Pharmaceutical Pipeline
Artificial intelligence is not just patching the holes in this old system; it’s building a new one from the ground up. By leveraging its ability to analyze colossal datasets, recognize complex patterns, and make highly accurate predictions, AI is transforming every single step of the drug development journey. This is the essence of the next gen drug discovery.
Step 1: Identifying the Target with Unprecedented Speed
The first step in fighting a disease is knowing your enemy. AI is a master detective, sifting through mountains of biological data—genomic sequences, protein structures, and clinical research papers—to pinpoint the precise biological targets that cause disease.
AI genomics medicine allows researchers to analyze an individual’s entire genetic makeup to find mutations or biomarkers linked to their condition. Machine learning models can then predict which of these are the most promising targets for a new drug. This accelerates the very foundation of the discovery process, ensuring researchers start on the right path from day one. Related: AI Revolutionizes Science: From Material Discovery to Personalized Medicine
Step 2: Designing the Perfect “Key” with Generative AI
Once a target is identified, the next challenge is creating a molecule—the drug—that can bind to it perfectly. In the past, this was a process of trial and error. Today, generative AI models, similar to those that create art and text, are being used for computational drug discovery.
These AI systems can:
- Design Novel Molecules: They can generate designs for entirely new drug candidates from scratch, optimized for properties like high efficacy and low toxicity.
- Refine Existing Compounds: They can take an existing molecule and suggest modifications to make it more effective or reduce side effects.
- Predict Interactions: AI can simulate how a potential drug will interact with its target in the body, a process known as
in silicomodeling, saving immense time and resources on physical lab experiments.
This is a monumental leap, enabling the creation of novel drug candidates AI has specifically designed for the task, rather than just discovered by chance.
Step 3: Advanced Screening and Predicting Success
With the ability to design millions of potential drug molecules virtually, the next step is figuring out which ones are worth pursuing. This is where advanced drug screening with AI comes in.
Instead of painstakingly testing compounds in petri dishes, AI platforms can run millions of virtual experiments simultaneously. They predict a molecule’s properties:
- Efficacy: How well will it work?
- Toxicity: Is it likely to be harmful?
- Metabolism: How will the body process it?
- Bioavailability: Will it reach the target area in the body effectively?
This predictive power allows scientists to focus only on the most promising candidates, drastically reducing the failure rate in later, more expensive stages of development. Related: AI Unleashed: Revolutionizing Money with Smart Personal Finance

Step 4: Supercharging Clinical Trials
The clinical trial phase has long been the biggest bottleneck in drug development. It’s slow, incredibly expensive, and where most drugs fail. AI clinical trials optimization is changing the game by bringing new levels of efficiency and insight.
AI contributes in several key ways:
- Smarter Patient Recruitment: AI can analyze medical records and genetic data to find the ideal candidates for a trial, ensuring the study has the right participants to yield clear results.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models can predict which patients are most likely to respond positively to a treatment or experience adverse effects, allowing for more personalized trial protocols.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Wearable devices and AI-powered software can monitor trial participants remotely, collecting continuous data and flagging potential issues early.
- Optimizing Dosages: AI can help determine the optimal dosage for different patient populations, increasing the chances of success and patient safety.
By making clinical trials smarter and more targeted, AI is directly responsible for faster drug development and getting life-saving therapies into the hands of patients sooner.
The Heart of the Revolution: AI-Powered Precision Medicine
The ultimate goal of all this technological advancement is to achieve precision medicine. This is a healthcare model that tailors medical decisions, practices, interventions, and products to the individual patient. Instead of a one-drug-fits-all approach, it’s about delivering the right treatment to the right patient at the right time.
Related: AI in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Medicine and Patient Care
From Broad Strokes to Personal Portraits: The Power of Personalized Drug Therapy
Imagine two people diagnosed with lung cancer. In the past, they would likely receive the same standard chemotherapy. Today, with AI genomics medicine, we can sequence their tumors and discover they are driven by entirely different genetic mutations.
AI-driven platforms can then match each patient’s unique biological profile to the most effective treatment. Patient A might benefit from a targeted therapy drug that blocks their specific mutation, while Patient B’s profile might indicate that immunotherapy is the best course of action. This is the core of precision oncology AI, one of the most advanced fields in personalized medicine.
This level of personalization leads to dramatically better outcomes, fewer side effects, and a more efficient use of healthcare resources. It transforms patient care from a guessing game into a precise, data-driven science.

Smart Drugs and Intelligent Drug Delivery
The AI biotech future is pushing the boundaries even further with concepts like smart drug technology and intelligent drug delivery. These are systems designed to deliver a therapeutic agent only to the diseased cells or tissues, leaving healthy cells untouched.
Think of it like a smart-bomb for disease. Researchers are developing nanoparticles that can be loaded with a drug and programmed to seek out cancer cells based on their unique molecular signatures. Once they arrive at their destination, they release their payload, maximizing the drug’s impact on the tumor while minimizing collateral damage to the rest of the body. This is a critical step in creating powerful AI driven therapeutics that are both potent and gentle.
Real-World Impact: AI Drug Discovery in Action
This isn’t just theory; AI healthcare breakthroughs are happening now. Companies are already bringing AI-discovered drugs to market in record time.
A landmark example comes from Insilico Medicine, which used its generative AI platform to identify a novel target and design a new drug for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), a chronic lung disease. The entire process, from target discovery to the start of Phase 1 clinical trials, took less than 30 months—a fraction of the industry average.
Another powerful application is drug repurposing AI. Many existing drugs are approved as safe but may have undiscovered benefits for other diseases. AI algorithms can rapidly scan vast databases of drug and disease information to find these hidden connections. This is one of the fastest and most cost-effective AI driven health solutions, as it allows us to find new uses for old drugs, bypassing much of the early-stage development process. Related: The AI-Powered Smart Home: Revolutionizing Efficiency, Security, and Convenience in 2024
Navigating the New Frontier: Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Like any revolutionary technology, the rise of AI in medicine is not without its challenges. To responsibly harness its power, we must navigate these hurdles with care and foresight.
The Data Dilemma
AI is hungry for data. The success of machine learning drug research depends on access to massive, high-quality, and diverse datasets. This raises critical questions about patient privacy, data security, and algorithmic bias. If AI models are trained primarily on data from one demographic, their predictions may not be accurate for others, potentially widening health disparities. Related: How AI is Revolutionizing Cybersecurity and Protecting Our Digital World
The “Black Box” Problem
Some of the most powerful AI models, particularly in deep learning, can be “black boxes.” This means they can produce an incredibly accurate prediction, but it’s not always clear how they arrived at that conclusion. In medicine, where lives are at stake, this lack of transparency can be a major barrier to trust and adoption for both doctors and regulatory agencies.
Regulation and the Human Element
The ethical AI in medicine conversation is paramount. How do regulatory bodies like the FDA evaluate and approve a drug that was designed by an algorithm? We need new frameworks to validate the safety and efficacy of these AI-driven therapies.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to remember that AI is a tool to empower human experts, not replace them. The future of medicine AI is a collaborative one, where the computational power of machines augments the wisdom, empathy, and ethical judgment of scientists and clinicians.
Conclusion: A New Dawn for Health and Medicine
The integration of artificial intelligence into pharmaceutical R&D is more than just an upgrade—it’s a complete reinvention of how we discover, develop, and deliver medicine. We are at the dawn of an era where treatments are no longer one-size-fits-all but are as unique as the individuals they are designed to help.
From accelerating the fight against AI for chronic diseases like Alzheimer’s and diabetes to pioneering patient-specific treatments for rare cancers, the impact is profound. The journey from a costly, decade-long marathon to a faster, more precise, and more intelligent sprint is well underway. The fusion of AI and medical research promises not just better drugs, but a fundamentally healthier and more equitable future for humanity.
The precision revolution is here, and it’s being written in the language of data, algorithms, and a relentless drive to improve human health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is AI drug discovery?
AI drug discovery is the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to accelerate and improve the process of finding and developing new medicines. It involves using algorithms to analyze vast biological datasets, identify disease targets, design novel drug molecules, predict their effectiveness and safety, and optimize clinical trials, making the entire process faster, cheaper, and more successful.
Q2. How is AI used in precision medicine?
In precision medicine, AI analyzes a patient’s unique genetic, lifestyle, and environmental data to predict which treatments will be most effective for them. It helps doctors select the right drug at the right dose for the right person, moving away from a “one-size-fits-all” approach. This is particularly impactful in oncology, where AI can match a tumor’s genetic profile to a specific targeted therapy.
Q3. What are the main benefits of using AI in drug development?
The main benefits are speed, cost reduction, and higher success rates. AI can shorten the drug discovery timeline from over a decade to just a few years. It drastically cuts R&D costs by reducing the need for expensive lab experiments and preventing failures late in the process. Most importantly, it leads to the development of more effective and safer AI driven therapeutics tailored to specific patient populations.
Q4. Can AI replace human scientists in pharmaceutical R&D?
No, AI is a powerful tool designed to augment, not replace, human scientists. While AI can handle massive data analysis and computation far beyond human capabilities, it lacks the creativity, critical thinking, ethical judgment, and real-world intuition of experienced researchers and clinicians. The future of AI in pharmaceutical R&D is a collaborative model where human experts guide and interpret the insights generated by AI.
Q5. What is drug repurposing, and how does AI help?
Drug repurposing (or repositioning) is the process of finding new therapeutic uses for existing, already-approved drugs. AI excels at this by rapidly scanning massive databases of scientific literature, clinical trial data, and molecular information to identify potential connections between an existing drug and a new disease. This is a much faster and cheaper path to new treatments because the drug’s safety profile is already known.
Q6. What are the ethical challenges of AI in medicine?
Key ethical challenges include data privacy and security, as AI models require vast amounts of sensitive patient health information. Another is algorithmic bias; if AI is trained on non-diverse data, it could perpetuate or worsen health disparities. Finally, the “black box” nature of some AI models raises issues of accountability and transparency when making critical healthcare decisions, highlighting the need for strong ethical AI in medicine frameworks.