AI’s Medical Leap: Accelerating Drug Discovery & Clinical Trials

For decades, the journey of a new drug from a lab concept to a patient’s hands has been a marathon—a slow, incredibly expensive, and often-failing endeavor. On average, it takes over a decade and costs upwards of $2.6 billion to bring a single new medicine to market, with a failure rate hovering above 90%. But what if we could fundamentally change this equation? What if we could sprint through parts of that marathon, predict failures before they happen, and design treatments with pinpoint accuracy?
This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality being forged by the fusion of artificial intelligence and medical science. Artificial intelligence in pharma is no longer a futuristic buzzword; it’s a powerful engine driving one of the most significant transformations in healthcare history. From identifying the root causes of disease at a genetic level to designing novel drug compounds and streamlining human trials, AI is supercharging the entire AI drug development pipeline.
In this deep dive, you’ll learn exactly how AI speeds up drug discovery, explore the groundbreaking AI biotech applications in clinical trials, and understand the profound impact of this technology on the future of personalized medicine and healthcare research.
The Traditional Drug Discovery Pipeline: A Slow and Costly Marathon
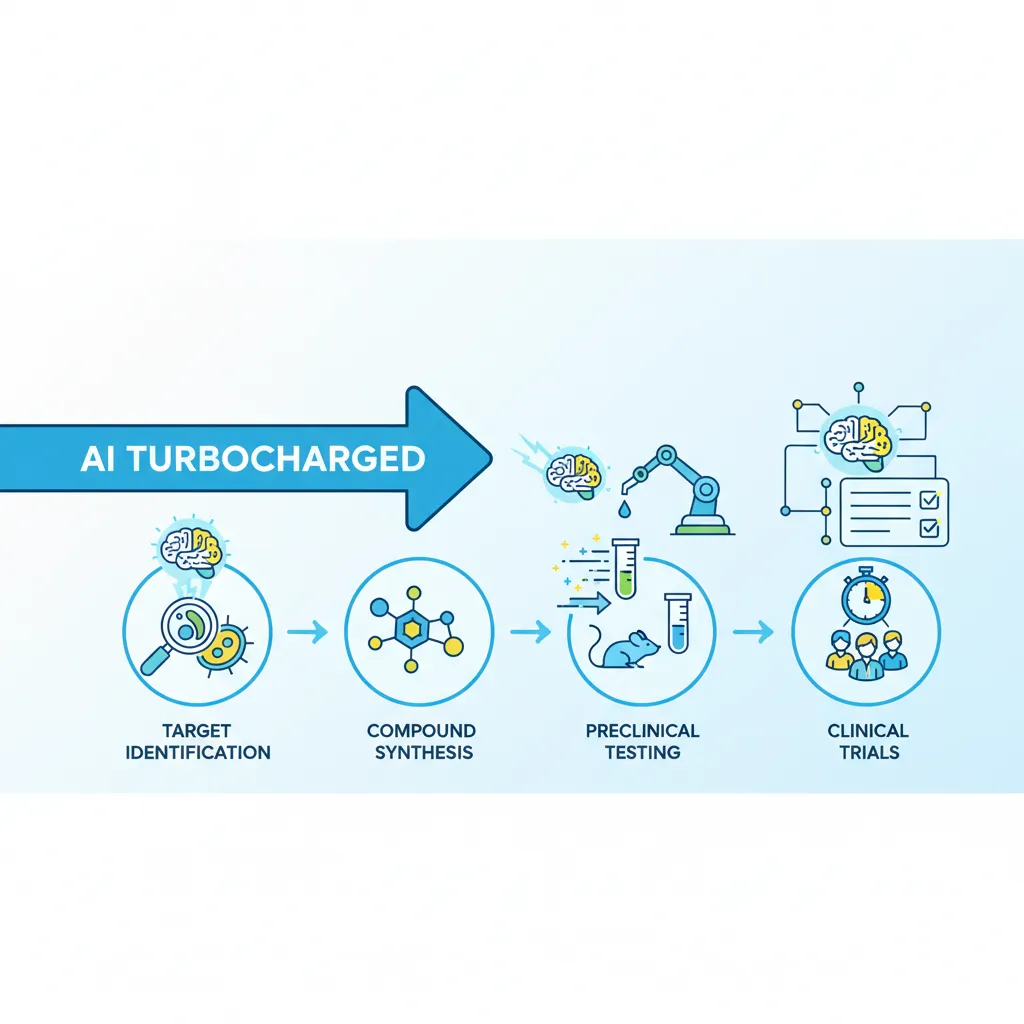
To appreciate the scale of AI’s impact, we first need to understand the mountain it’s helping us climb. The traditional path to a new drug is a linear, multi-stage process fraught with risk and uncertainty.
- Target Identification & Validation: Scientists spend years trying to find a specific biological target—like a protein or gene—that plays a crucial role in a disease. This involves painstakingly combing through biological data and conducting countless lab experiments.
- Hit Discovery & Lead Optimization: Once a target is validated, the search begins for a “hit”—a molecule that can interact with the target. Researchers screen millions of compounds, a process akin to finding a single specific key for a single specific lock in a warehouse full of keys. The promising “hits” are then chemically modified (“optimized”) to improve their effectiveness and reduce side effects.
- Preclinical Testing: The optimized lead compounds are tested in labs and on animal models to assess their safety and efficacy. This phase alone can take several years, and many promising candidates fail here due to unforeseen toxicity.
- Clinical Trials (Phases I, II, III): If a drug passes preclinical tests, it moves to human trials, a three-phase process that can take 6-7 years. This is the most expensive and time-consuming part, requiring thousands of patients and meticulous data collection to prove the drug is safe and works better than existing treatments.
- Regulatory Approval & Post-Market Surveillance: Finally, a mountain of data is submitted to regulatory bodies like the FDA for approval. The journey doesn’t even end there, as the drug’s performance is monitored long after it hits the market.
This process is a funnel of attrition. For every 10,000 compounds that start the journey, only one will typically make it to market. This is the paradigm that AI drug discovery is shattering.
How AI is Revolutionizing Every Stage of Drug Development
Instead of just making the old process faster, AI-driven drug research is reinventing it from the ground up. By leveraging machine learning, deep learning, and now generative AI, scientists can analyze vast datasets, predict outcomes, and generate novel ideas at a speed previously unimaginable.
Stage 1: Identifying Disease Targets with Unprecedented Precision
The first step in curing a disease is understanding it. AI algorithms excel at finding patterns hidden within massive biological datasets—genomics, proteomics, and clinical records. This is a game-changer for AI for disease target identification.
- Data Mining: AI can sift through petabytes of scientific literature, patient data, and genetic information to identify novel correlations between genes and diseases that human researchers might miss.
- Predictive Modeling: Machine learning models can predict which biological targets are most “druggable,” meaning they are more likely to respond to therapeutic intervention. This allows research to focus on the most promising avenues, saving immense time and resources.
By starting with a better, more validated target, the entire subsequent pipeline has a higher chance of success.
Stage 2: Designing Novel Drug Compounds with Generative AI
This is where the revolution truly kicks into high gear. Instead of screening existing compounds, generative AI drug discovery allows scientists to design entirely new molecules from scratch, tailored to a specific disease target.

Think of it like an architect using an AI to generate thousands of unique, structurally sound building blueprints based on a set of constraints (location, materials, size). Similarly, generative models like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformers can:
- Generate Novel Molecules: Create vast libraries of virtual compounds with desired properties.
- Optimize for Efficacy: Predict a molecule’s binding affinity to its target, ensuring it will be effective.
- Design for Safety: Simultaneously optimize for low toxicity and good metabolic properties (how the body processes it).
Companies like Insilico Medicine and Absci are already using these AI-powered drug design platforms to create new drug candidates in months, not years. This radical acceleration is a core benefit of machine learning drug discovery.
Stage 3: Predicting Efficacy and Safety with AI Toxicology
One of the most heartbreaking points of failure in drug development is the preclinical or early clinical stage, where a promising drug is found to be toxic. AI in toxicology prediction aims to front-load this safety analysis.
Deep learning models can be trained on vast databases of known compounds and their toxicological profiles. By analyzing a new molecule’s structure, the AI can predict its potential toxicity with a high degree of accuracy before it’s ever synthesized in a lab. This “fail fast, fail cheap” approach prevents researchers from wasting years on a compound destined to fail.
Stage 4: Repurposing Existing Drugs for New Diseases
Why reinvent the wheel if you don’t have to? AI drug repurposing involves using artificial intelligence to scan existing, approved drugs to see if they could be effective against other diseases. Since these drugs have already been proven safe for human use, this strategy dramatically shortens the development and approval timeline. AI algorithms can connect the dots between a drug’s mechanism of action and the biological pathways of different diseases, uncovering non-obvious therapeutic opportunities.
Accelerating Clinical Trials: From Recruitment to Analysis
The impact of AI on drug discovery extends far beyond the lab. The clinical trial phase, traditionally a major bottleneck, is being completely transformed by AI in clinical trials. This is where AI helps bridge the gap between a promising compound and a life-saving treatment.
Optimizing Patient Recruitment and Stratification
Finding the right patients for a clinical trial is one of the biggest challenges. It’s often the primary reason for trial delays. AI streamlines this process:
- Smart Recruitment: AI can analyze electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, and genetic data from millions of patients to identify the ideal candidates for a specific trial in minutes.
- Patient Stratification: Machine learning can identify subgroups of patients who are most likely to respond to a particular treatment. This leads to smaller, more targeted, and more successful trials, which is a cornerstone of AI in precision medicine. Related: Decoding Investor Psychology: How AI Uncovers Behavioral Biases
Enhancing Data Analysis and Endpoint Detection
Modern clinical trials generate a staggering amount of data, from wearable sensor readings to complex medical imagery. AI is essential for making sense of it all.
- Real-time Monitoring: Wearable devices and sensors monitored by AI can track patient vitals and treatment side effects continuously, providing a much richer dataset than periodic clinic visits.
- Automated Analysis: AI can analyze medical images (like MRIs or CT scans) to detect subtle changes or disease progression more accurately and consistently than the human eye.
- Predictive Analytics: AI models can predict which patients might drop out of a trial or experience adverse effects, allowing for proactive intervention.
The Rise of Personalized and Precision Medicine
Perhaps the most exciting outcome of pharmaceutical AI innovation is the push towards truly personalized medicine. By integrating a patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors, personalized medicine AI can help tailor treatments specifically for them.

Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, doctors can use AI-driven insights to prescribe the right drug, at the right dose, for the right person. This not only maximizes the chance of a positive outcome but also minimizes the risk of side effects, representing a true paradigm shift in patient care.
The Tangible Benefits: Measuring the Impact of AI in Pharma
The adoption of AI is not just a theoretical exercise; it’s delivering measurable results that are reshaping the economics and timeline of medical research.
Drastically Reducing R&D Costs and Timelines
The core promise of accelerating drug development with AI is being realized. By automating tasks, predicting failures early, and optimizing trial design, AI is significantly reducing R&D costs pharma companies face. Some reports suggest AI can shave years off the development timeline and reduce costs by 25-50%. This frees up capital for more research and could ultimately lead to more affordable medicines. Related: AI-Powered Algorithmic Trading: The Future of Market Prediction
Increasing the Success Rate of New Drugs
By improving target selection, designing better molecules, and running more efficient trials, AI directly tackles the staggering 90% failure rate. Even a modest improvement in the success rate translates into more life-saving drugs reaching the market each year, marking one of the most significant pharmaceutical AI breakthroughs.

Fostering an Ecosystem of AI Innovation
The rise of specialized drug discovery platforms AI has created a vibrant ecosystem of AI-first biotech companies. These nimble startups and established tech giants are collaborating with pharmaceutical companies to push the boundaries of what’s possible, ensuring the future of drug development AI remains bright and competitive. This technological race is not just about profits; it’s about pioneering the next generation of cures. Related: GPT-4o vs. Project Astra: The Multimodal AI Showdown
Navigating the Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the promise is immense, the path to fully integrating AI into medicine is not without its hurdles. Addressing these challenges transparently is crucial for building trust and ensuring equitable outcomes.
Data Quality, Privacy, and Bias
AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. High-quality, diverse, and well-curated datasets are essential. There are significant concerns around:
- Patient Privacy: Using sensitive health data requires robust anonymization and security protocols.
- Algorithmic Bias: If training data is not representative of the global population, AI models could develop biases, leading to drugs that are less effective for certain demographic groups.
Regulatory Hurdles and the Path to Approval
Regulatory bodies like the FDA are working to adapt their frameworks to evaluate drugs developed using AI. Establishing clear guidelines for AI for faster drug approval is a work in progress. How do you validate a drug designed by an AI? This question requires new standards for transparency and validation.
The “Black Box” Problem and Explainable AI (XAI)
Some complex deep learning models operate as “black boxes,” meaning even their creators don’t know exactly how they arrive at a particular conclusion. In medicine, this is a major issue. The field of Explainable AI (XAI) is focused on developing models that can provide clear reasoning for their predictions, a critical step for gaining the trust of doctors, regulators, and patients. Related: AI in Education: Revolutionizing Personalized Learning and Future Skills
Conclusion: A New Era of Hope in Medical Research
The integration of artificial intelligence into drug discovery and clinical trials is more than just an incremental improvement—it is a fundamental paradigm shift. We are moving from a process of slow, serendipitous discovery to one of intentional, data-driven design. AI is transforming medical research by making it faster, cheaper, and more effective.
By empowering scientists to understand diseases at an unprecedented depth, design novel therapies with molecular precision, and run smarter clinical trials, AI is not only accelerating the development of new medicines but also paving the way for a future of truly personalized healthcare. The challenges of data, ethics, and regulation are real, but the momentum is unstoppable. We stand at the dawn of a new era of hope, where the medicines of tomorrow will be discovered and delivered with the power and speed of AI.
FAQs
Q1. What is AI drug discovery?
AI drug discovery is the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to accelerate the process of identifying and developing new medicines. It involves using algorithms to analyze complex biological data, predict drug-target interactions, design novel molecular compounds, and optimize clinical trials, making the entire process faster, cheaper, and more successful.
Q2. How does AI speed up the drug discovery process?
AI speeds up drug discovery in several key ways: it rapidly analyzes vast datasets to identify disease targets in weeks instead of years; it uses generative models to design millions of potential drug candidates virtually; it predicts a drug’s toxicity and efficacy early, reducing late-stage failures; and it optimizes clinical trials by finding suitable patients faster.
Q3. What are the main benefits of using AI in pharma?
The primary benefits of AI in the pharmaceutical industry include a significant reduction in R&D costs and timelines, a higher success rate for drugs entering clinical trials, the ability to design novel drugs for previously “undruggable” targets, and the acceleration of personalized medicine tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup.
Q4. What companies are using AI for drug discovery?
Many innovative companies are leading the charge in AI drug discovery. This includes specialized AI-biotech firms like Schrödinger, Exscientia, Insilico Medicine, and Recursion Pharmaceuticals, as well as major pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer, Novartis, and AstraZeneca, who are increasingly partnering with or building their own AI platforms.
Q5. What is generative AI in drug discovery?
Generative AI in drug discovery refers to AI models that can create something new, rather than just analyzing existing data. These algorithms can design entirely novel molecular structures from scratch that are optimized to bind to a specific disease target and have desirable drug-like properties, dramatically accelerating the creative part of drug development.
Q6. What are the ethical considerations of AI in drug discovery?
Key ethical considerations include ensuring patient data privacy and security, preventing algorithmic bias from unrepresentative training data (which could lead to drugs that don’t work for all populations), ensuring transparency and explainability in AI decision-making (the “black box” problem), and establishing clear regulatory pathways for AI-developed drugs.