AI for Mars Colonization: Building Humanity’s Next Home
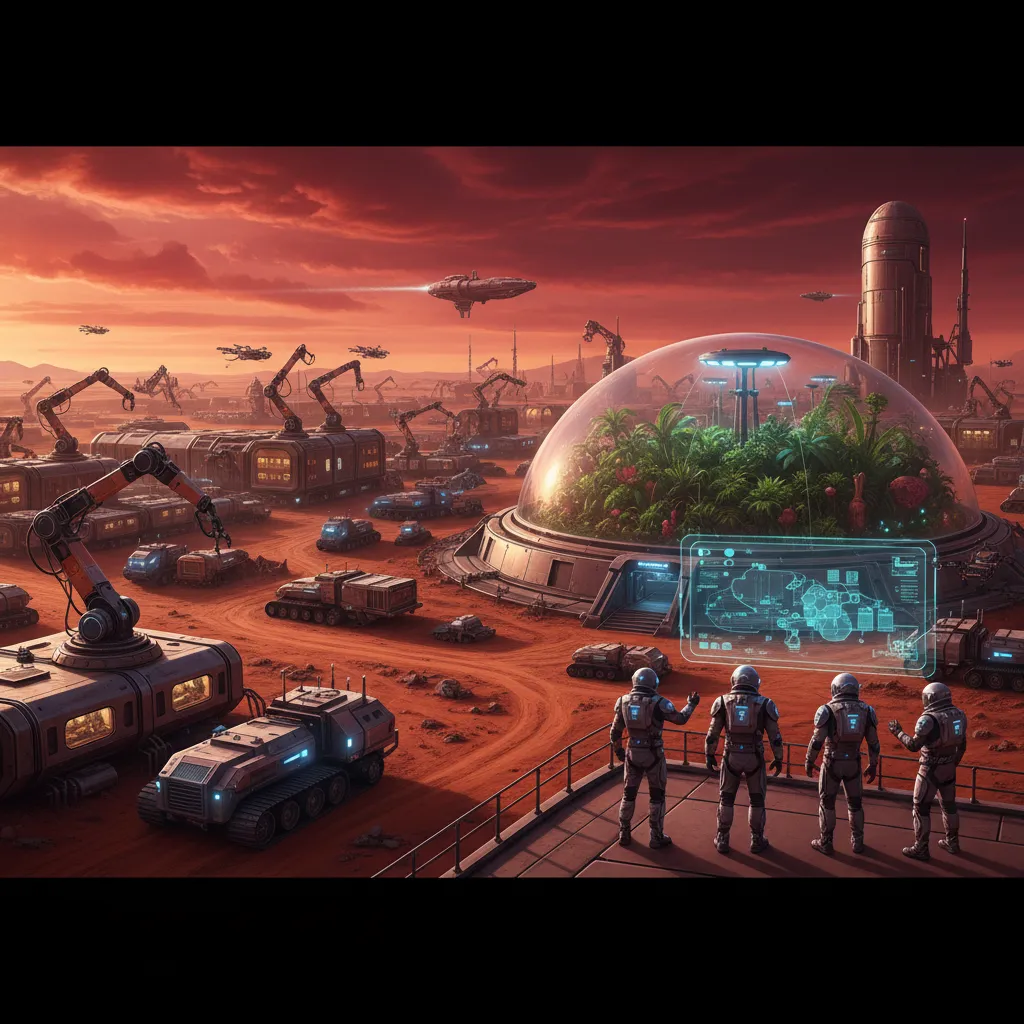

The dream of humanity setting foot on Mars, of seeing Earth rise over the crimson horizon, is no longer confined to science fiction. It’s a tangible goal that the brightest minds in science and engineering are working towards. But the challenges are monumental. Mars is an unforgiving world with a thin atmosphere, lethal radiation, and extreme temperatures. Sending humans to build a home there is perhaps the most complex undertaking our species has ever contemplated.
The solution? We send the builders first. Not human builders, but an army of intelligent, autonomous systems. Artificial intelligence is the critical key that will unlock our future as a multi-planetary species. AI Mars colonization isn’t just about smarter rovers; it’s about creating a foundational intelligence that can build, manage, and sustain a human presence millions of miles from home.
In this deep dive, we’ll explore the indispensable role of AI in every facet of Martian settlement. From robotics for Mars construction laying the groundwork for our arrival to sophisticated AI managing the very air we’ll breathe, you’ll discover how these advanced systems are making humanity’s next giant leap possible. This is the story of how AI will colonize Mars, transforming a desolate landscape into humanity’s next home.
Why Mars is the Ultimate AI Proving Ground
Before we can understand the solutions AI provides, we must first appreciate the sheer scale of the problem. Mars is not Earth’s friendly neighbor. It’s a hostile environment where a single mistake can be catastrophic.
Three fundamental challenges make direct human control impossible and elevate AI from a helpful tool to an absolute necessity:
- The Hostile Environment: The Martian surface is bombarded with cosmic radiation. Its atmosphere is 95% carbon dioxide and just 1% the thickness of Earth’s. Temperatures can plummet to -200°F (-128°C). Fine, abrasive dust clogs machinery and can be toxic to humans. Operating in this environment requires systems that are resilient, predictive, and can perform self-repair without human intervention.
- The Great Communication Delay: Light itself takes between 4 and 22 minutes to travel from Earth to Mars. This isn’t lag; it’s a fundamental law of physics. You can’t joystick a robot in real-time when your command arrives 20 minutes late. Any system operating on Mars must be a true autonomous systems space platform, capable of making its own decisions, solving complex problems, and adapting to unforeseen circumstances without waiting for instructions.
- The Scale of the Task: Building a self-sustaining colony—habitats, power grids, resource processing plants, and farms—is a colossal engineering project. The cost and risk of sending human crews for this initial construction phase are astronomical.
These challenges create the perfect crucible for developing the next generation space AI. Mars forces us to create systems that are not just smart, but truly independent, resourceful, and robust—paving the way for future AI in deep space exploration.
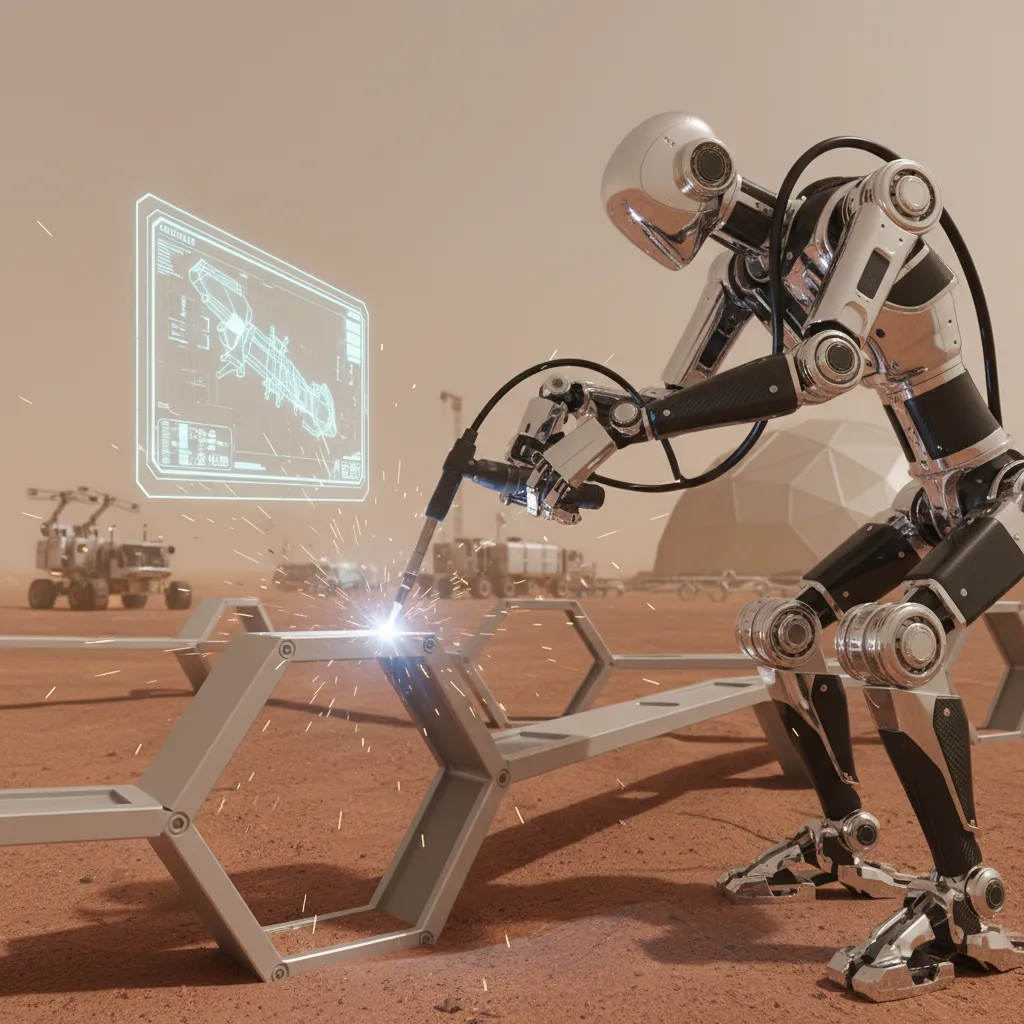
The Vanguard: AI-Powered Robots Laying the Foundation
The first pioneers on Mars won’t have human faces. They will be swarms of AI-driven robots, the tireless architects and laborers of our first off-world settlement. Their primary mission: to build a safe, operational, and automated Mars base before the first human crew even begins their journey.
Autonomous Construction and Habitat Building
The most immediate application of AI in space exploration is construction. We can’t simply ship a pre-fabricated base from Earth; it’s too heavy and inefficient. Instead, we’ll use the Martian environment itself as our building material, a concept known as In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU).
This is where AI and off-world construction truly shines. Fleets of AI-powered robots will:
- Excavate and Prepare: Autonomous bulldozers and excavators will level terrain, dig foundations, and prepare construction sites with precision guided by 3D geological maps.
- Harvest Regolith: Specialized rovers will scoop up Martian soil (regolith), the primary ingredient for construction.
- 3D Print Structures: Large-scale 3D printers, managed by a central AI, will use a mixture of regolith and binding polymers to print everything from habitat shells and landing pads to radiation shields and equipment storage. This process of AI habitat building Mars is one of the most promising Mars settlement technology advancements.
- Assemble and Install: Robotic arms and cranes will install complex components shipped from Earth, like windows, airlocks, and internal systems, with superhuman precision.
This AI-managed construction crew works 24/7, undeterred by radiation or dust storms, ensuring a safe haven is ready for the human arrivals. Related: The Rise of Autonomous AI Agents: Revolutionizing Work
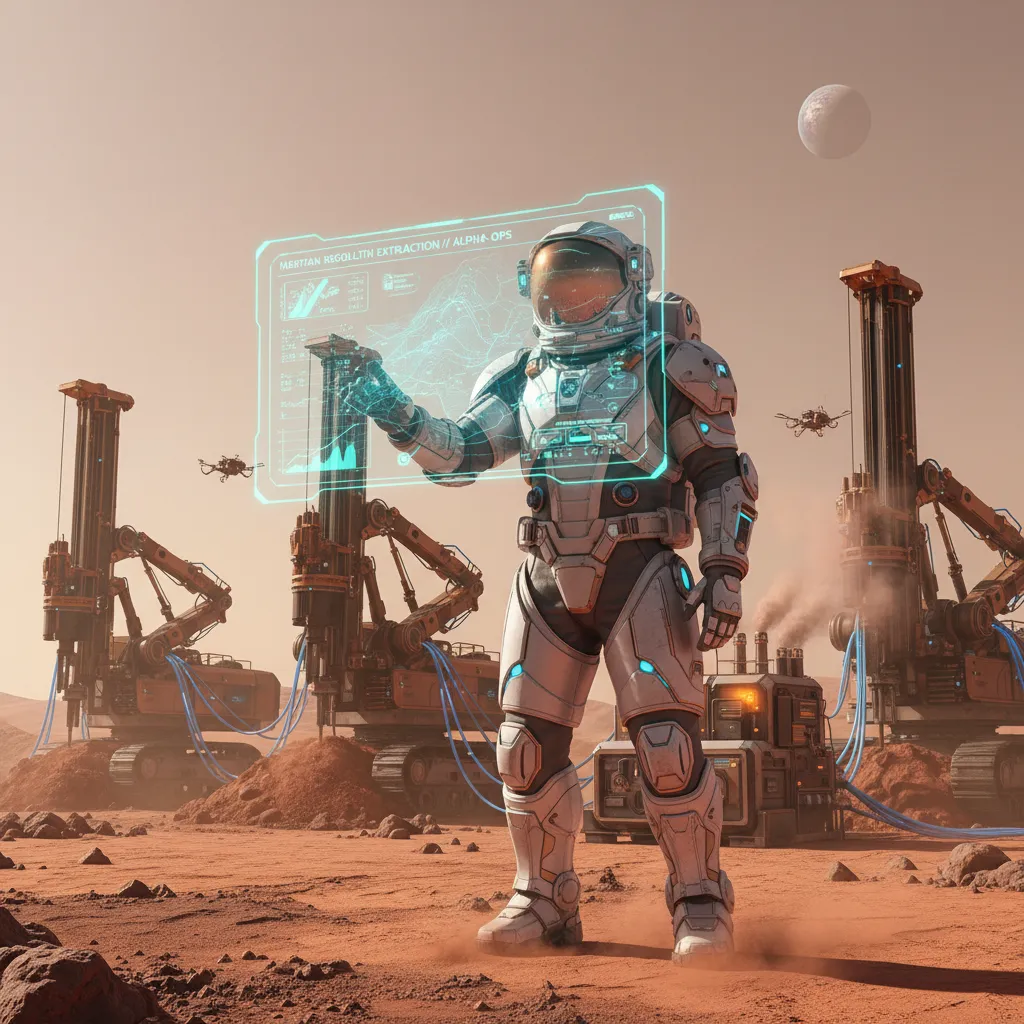
Smart Resource Extraction and Utilization (ISRU)
A colony can’t survive on supplies from Earth alone. It must live off the land. AI driven space resource utilization is the engine that will make this possible. Before a single habitat is printed, AI-powered orbiters and rovers will be prospecting the planet.
Machine learning algorithms will analyze terabytes of satellite imagery and ground-penetrating radar data to pinpoint the most promising locations for vital resources:
- Water Ice: The lifeblood of any colony. AI will identify subterranean ice deposits, which can be mined to provide water for drinking, growing crops, and creating rocket fuel.
- Minerals and Metals: AI systems on rovers like the Perseverance use spectrometers to identify rock compositions, searching for iron, aluminum, silicon, and other materials essential for manufacturing and repairs.
- Atmospheric Harvesting: The thin Martian atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide, but it’s a valuable resource. AI will manage systems like the MOXIE experiment on Perseverance, but on a massive scale. This AI oxygen generation Mars technology will provide breathable air for habitats and oxidizer for rockets, a critical step for a return journey to Earth.
This entire process, from discovery to processing, represents a paradigm shift in AI resource extraction space, turning a barren planet into a source of sustenance.

Engineering a Habitable Haven: AI as the Life Support Architect
Once the physical structures are built, the next monumental task is to turn them into a place where humans can live and thrive. This is where AI transitions from a construction foreman to the central nervous system of the colony, ensuring AI for sustainable Mars living.
The AI Biosphere: Smart Habitats and Life Support
The first Martian homes will be marvels of engineering—smart habitats Mars style. Every critical system will be monitored, managed, and optimized by a sophisticated AI network. This is the domain of AI life support systems space, a constant, vigilant intelligence ensuring the survival of the crew.
This AI will be responsible for:
- Atmosphere Regulation: Constantly monitoring oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and trace gas levels, making micro-adjustments to keep the air perfectly balanced and safe.
- Water Recycling: Managing a closed-loop system that purifies and reclaims every drop of water from breath, sweat, and wastewater—a process far too complex and critical to be left to manual control.
- Power Management: Optimizing energy distribution from solar panels and potential nuclear sources, routing power where it’s needed most and predicting consumption patterns to avoid blackouts.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using machine learning space colonization models, the AI will analyze sensor data from thousands of components to predict failures before they happen, dispatching repair drones or alerting the crew to potential issues.
This intelligent infrastructure transforms a simple shelter into a responsive, living environment, crucial for long-term AI for planetary habitation. Related: Transform Your Home with AI-Powered Smart Living
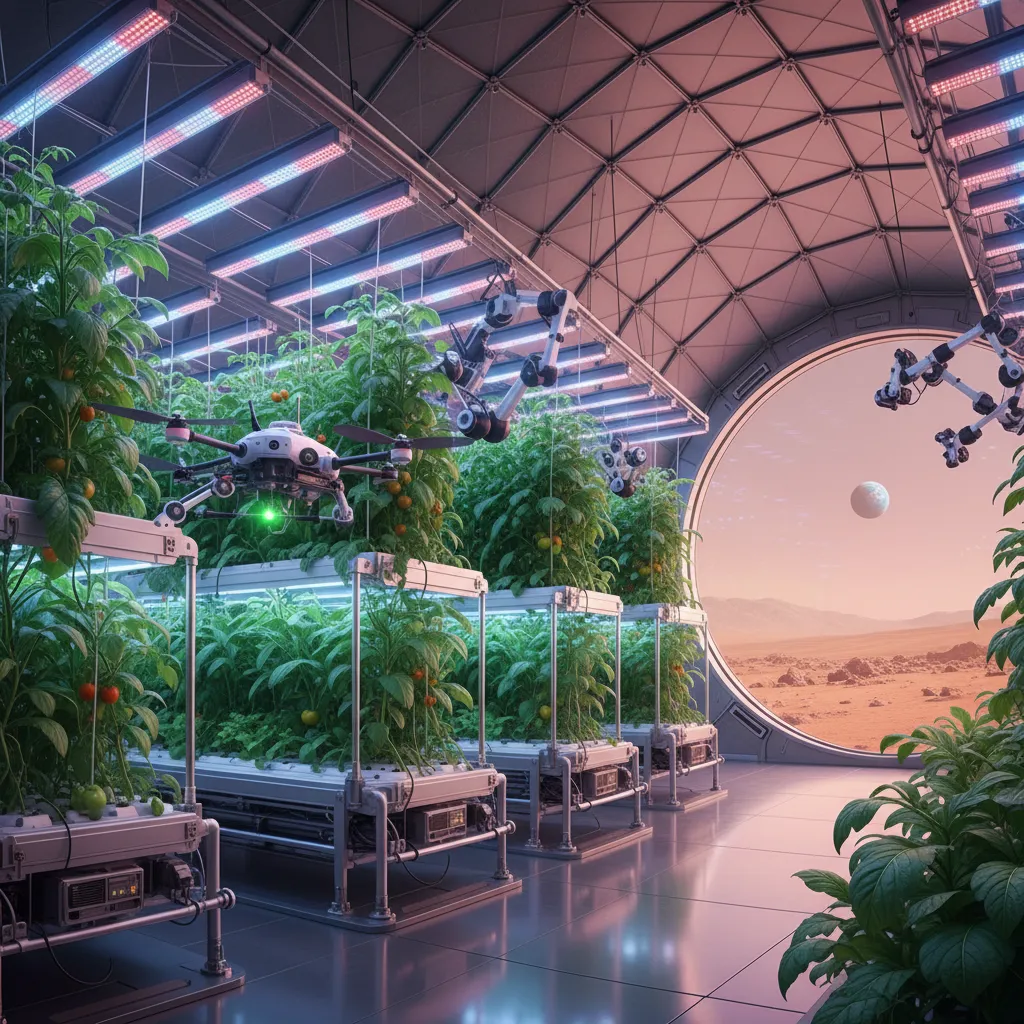
AI-Powered Martian Farming
Food is a cornerstone of self-sufficiency. Shipping freeze-dried meals for years is not a sustainable plan. The future of Martian dining lies in AI-managed agriculture inside pressurized biodomes.
Growing crops in an alien environment presents unique challenges, from different gravity to the lack of natural soil and pollinators. AI provides the solution:
- Precision Hydroponics: AI will control advanced hydroponic and aeroponic systems, delivering precisely tailored nutrient mists to plant roots.
- Optimized Growth Cycles: LED lighting systems will be managed by AI to provide the exact spectrum and intensity of light plants need at each stage of growth, mimicking ideal conditions on Earth and accelerating crop yields.
- Automated Health Monitoring: Cameras and sensors will constantly scan crops for signs of disease, nutrient deficiency, or stress. The AI can diagnose problems instantly and adjust nutrient or water delivery to a specific plant, preventing crop failures.
In a sense, this is micro-Martian terraforming AI, creating perfect, Earth-like oases within the harsh Martian landscape, ensuring the colonists have a fresh, sustainable food source.

The Human-AI Partnership: Pioneering Mars Together
The ultimate goal of all this automation is not to replace humans, but to empower them. Once the human AI pioneers Mars crew arrives, AI’s role will shift again, becoming an indispensable partner, assistant, and guide in the exploration and settlement of this new world.
The AI Co-Pilot and Mission Specialist
Living and working on Mars will be incredibly demanding. Each astronaut will be a highly trained scientist, but they can’t be an expert in everything. AI astronaut assistance will fill the gaps, acting as a cognitive multiplier for the crew.
- Intelligent Assistant: An AI, accessible via voice commands or augmented reality displays in helmets, will serve as a universal knowledge base. An astronaut could ask, “What is the mineral composition of this rock?” or “Show me the procedure for recalibrating the life support scrubber,” and receive instant, context-aware information.
- Health Monitoring: Wearable biosensors will track astronauts’ vital signs, stress levels, and exposure to radiation. The AI will analyze this data in real-time, flagging potential health issues long before they become serious and suggesting countermeasures. Related: Wearable AI: Reshaping Productivity and Daily Life
- System Operations: The AI will handle thousands of routine monitoring and system management tasks, freeing up the human crew from tedious work to focus on high-level research, exploration, and discovery.
This seamless human-AI collaboration is central to the future of Mars missions.
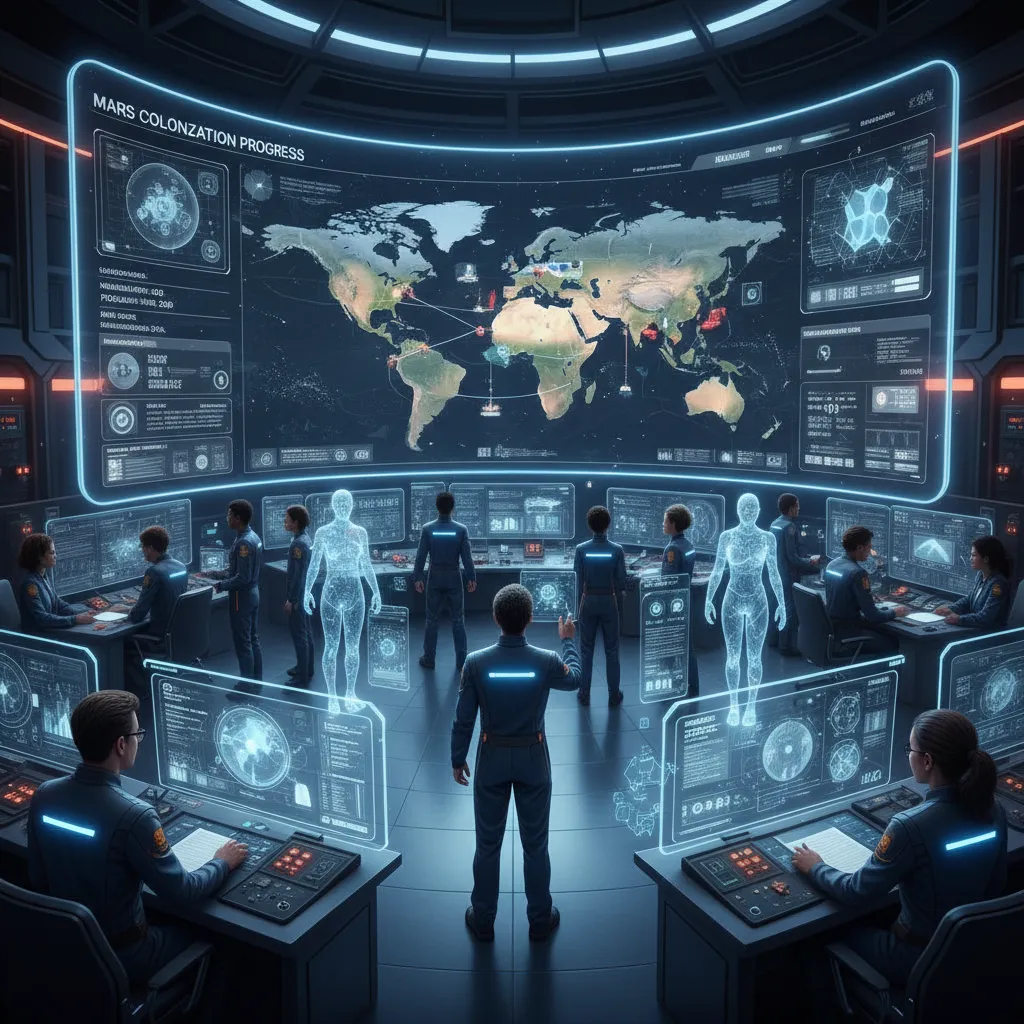

Navigating and Understanding a New World
Mars is a planet of mysteries. AI will be our chief interpreter, helping us understand the Martian environment AI is constantly analyzing. By processing vast datasets from orbital satellites, weather sensors, and geological surveys, AI will:
- Create Dynamic Maps: Generate high-resolution 3D maps of the surrounding terrain for rovers and human EVAs (Extra-Vehicular Activities), highlighting potential hazards like hidden crevices or unstable ground.
- Forecast Martian Weather: Predict the formation and movement of the planet’s infamous dust storms, providing crucial warnings to protect crews and equipment.
- Accelerate Scientific Discovery: AI algorithms will sift through scientific data, identifying patterns and anomalies that human eyes might miss. It can flag rocks with a high probability of containing evidence of past water or even microbial life, guiding scientists to the most promising areas for research.
Overcoming the Great Martian Filter: AI Challenges and Solutions
The path to an AI-driven Mars colony is not without its own monumental hurdles. These AI challenges Mars colonization presents are as complex as the Martian environment itself.
- Robustness and Reliability: An AI system on Mars cannot simply crash. It must be exceptionally fault-tolerant, capable of operating for years in a high-radiation environment with extreme temperature swings. Hardware must be radiation-hardened, and software must have multiple redundancies.
- Generalization and Adaptability: An AI trained on Earth data may not perform as expected under Martian conditions. These systems must be able to learn and adapt “on the fly” to a completely alien environment, dealing with situations its programmers never anticipated.
- Trust and Explainability (XAI): For humans to entrust their lives to an AI millions of miles away, they need to be able to understand its decisions. The “black box” problem, where even the creators don’t fully know why an AI made a certain choice, is unacceptable. Developing Explainable AI (XAI) that can justify its reasoning in human-understandable terms is a critical area of research.
Solving these challenges is not just key to Mars; it will drive incredible space robotics advancements and future AI space tech that will benefit us right here on Earth.
Conclusion: The Dawn of a New Human Era, Powered by AI
The colonization of Mars represents a fundamental turning point for humanity. It is our first step towards becoming a multi-planetary species, securing the long-term future of consciousness in the cosmos. This grand vision, however, rests on a foundation of intelligent automation.
From the first robotic surveyors to the complex systems that will sustain life and aid discovery, AI is the enabling technology at every step. The benefits of AI for Mars are not just about efficiency; they are about feasibility. AI will serve as the architect, the farmer, the doctor, and the vigilant guardian of our first off-world settlement.
The role of AI in Mars settlements is to take on the impossible tasks—the dangerous, the repetitive, and the monumentally complex—freeing humans to do what we do best: explore, dream, and push the boundaries of what’s possible. The crimson dust of Mars awaits, and when we arrive, we will do so on the shoulders of the intelligent machines we created to pave the way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How will AI be used to colonize Mars?
AI will be fundamental to every stage of Mars colonization. It will control autonomous robots for construction and 3D printing of habitats, manage resource extraction like mining for water ice, operate life support systems, oversee AI-powered farming inside biodomes, and act as an intelligent assistant to human astronauts, helping with everything from scientific analysis to health monitoring.
Q2. Can robots build a base on Mars before humans arrive?
Yes, absolutely. This is a core strategy for mitigating risk. Fleets of AI-powered robots, a key aspect of Mars settlement technology, will be sent ahead of humans to construct a fully functional and automated Mars base. They will use local Martian soil (regolith) to 3D-print habitats, build infrastructure, and ensure a safe environment is ready for the first human crew’s arrival.
Q3. How can AI help produce oxygen on Mars?
The Martian atmosphere is 95% carbon dioxide. AI will manage a process called In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) to generate oxygen. It will control instruments, similar to NASA’s MOXIE experiment, that electrochemically split carbon dioxide molecules into oxygen and carbon monoxide. AI oxygen generation Mars systems will run this process efficiently on a large scale to produce breathable air for habitats and rocket propellant.
Q4. What is the biggest challenge for AI on Mars?
The biggest challenge is achieving true, robust autonomy. Due to the significant communication delay between Earth and Mars (up to 22 minutes one-way), an AI cannot rely on human intervention. It must be able to make complex decisions, solve unforeseen problems, and recover from errors entirely on its own in a harsh and unpredictable environment, which is a major focus of AI challenges Mars colonization research.
Q5. What is ISRU and why is it important for Mars colonization?
ISRU stands for “In-Situ Resource Utilization,” which means using resources found on Mars itself rather than transporting everything from Earth. It’s crucial because it dramatically reduces the cost and complexity of a mission. AI driven space resource utilization will enable us to mine water ice, extract minerals from rocks, and produce oxygen and fuel from the atmosphere, making a long-term, sustainable colony possible.
Q6. Will AI replace human astronauts on Mars?
No, the goal is partnership, not replacement. AI will handle the most dangerous, repetitive, and data-intensive tasks, acting as a powerful tool to augment human capabilities. This AI astronaut assistance allows the human crew to focus on exploration, high-level scientific research, and critical decisions that require human ingenuity and intuition.
Q7. How will AI manage life support systems in a Mars habitat?
AI will act as the central nervous system for smart habitats on Mars. It will use a network of sensors to continuously monitor and regulate air quality, water purity, temperature, and pressure. Using machine learning, it will predict resource consumption, optimize energy usage, and even anticipate system failures before they occur, ensuring the habitat remains safe and livable for its human occupants.